Civil Society, Development & Aid, Editors’ Choice, Featured, Gender, Gender Violence, Global, Headlines, Health, Human Rights, Humanitarian Emergencies, Population, Sustainability, Sustainable Development Goals, TerraViva United Nations, Women’s Health
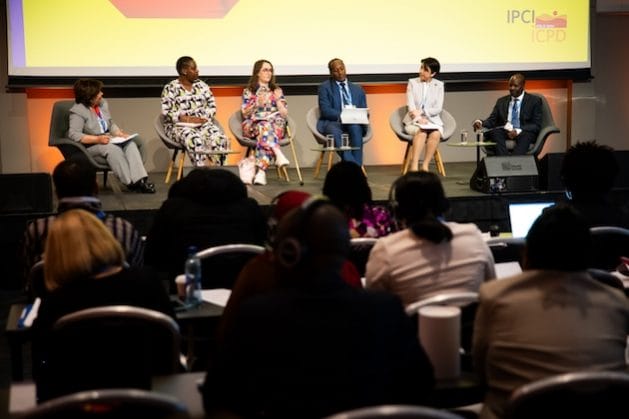

The benefits and challenges of technology in SRHR were a key topics at the International Parliamentarians’ Conference on Implementation of the ICPD Programme of Action 2024, in Oslo, Norway. Credit: Petter Berntsen / NTB Kommunikasjon
– Technology emerged as a core theme of IPCI Oslo for its relevance in advancing the objectives of the Cairo Programme of Action.
When channeled for good, it is an effective tool that can fill accessibility gaps in the health sector and spread awareness of sexual and reproductive health rights. Yet, the way in which digital technology has been weaponized against SRHR is of great concern for parliamentarians, especially for women.
In a plenary meeting on Thursday, April 11, 2024, parliamentarians shared their countries’ experiences of employing technology to enhance sexual and reproductive health practices (SRHR), while also cautioning its misuse as a tool to propagate misinformation and disinformation about SRHR and to enact online harassment, among other offenses. Information and communications technology was seen to be used often to raise awareness of reproductive and sexual health or to facilitate access to services.
Telemedicine is one example of the way that technology is used to enhance access to reproductive health services. Countries like Tanzania and Ireland saw an increased reliance on telemedicine and digital technology during the COVID-19 pandemic, when in-person appointments were not an option, along with an increased use of digital family planning apps that have allowed young women to make informed decisions.
It was acknowledged that uneven access to technology is a sign of and can result in inequalities in this sector, which can, as Fox Odoi-Oywelowo, a member of parliament from Uganda, remarked, hinder progress in the ICPD. Within the healthcare sector, this is evident in the skills and training of healthcare workers in urban areas versus rural areas. Rural areas already face the issue of fewer options for sexual and reproductive health services and fewer opportunities to develop digital skills, so this digital divide is further indicative of inequality.
Parliamentarians may find it challenging to uphold SRHR in the first place when vocal opponents of these rights are driving online discourse. Women in politics who advocate for these rights are often targets of harassment. Annie Hoey of Ireland’s Seanad Eirann Party recounted her own experience of harassment. She noted in such cases that not only was the politician attacked on an individual level, but the social issue would be attacked as well, and any person involved by association would face harassment online.
The impact of this on SRHR is that women in politics are threatened or prevented from doing their job. Developments in SRHR policies are drafted by women parliamentarians, often based on lived experiences, and women in politics have a public platform through which they can raise awareness on the issues. But if they are driven away from public life out of fear for their safety, the issues may not get picked up again. At the parliamentarian level, there would be no one to advocate for these rights to be enshrined.
Neema Lugangira, MP, Tanzania, said that this form of technology-facilitated gender-based violence on women in politics can cause them to retreat from online spaces, a form of “self-censorship,” which can “shrink democracy.”
“To get more women in politics, we need to be online,” she said. “If we want to truly take advantage of the paths to technology, which will impact more young women and girls who are mostly marginalized, we have to make these online spaces safe. Because how are we going to access the information if the online space is not safe?”
This also ties back to the concept of bodily autonomy and the right to live safely in one’s body. “If there are threats of violence online that can then become in-person, that is, I think, an impact on our sexual and reproductive health because we can’t live as fully,” Hoey told IPS.
She explained that she knew of women politicians who got abortions and had to be private about this in fear of facing judgement and scrutiny from critics online.
“All of this online discourse of demonizing women, demonizing women in politics… means that other elements of our lives are under threat. People should be able to access abortions whether they want to or not, whether they are women parliamentarians or not. This online discourse creates a lack of safety for women to do that.”
This is just one example of technology-facilitated gender-based violence (TF-GBV), where online harassment leads to a fear of safety for one’s life and even risks reducing women’s public presence.
UNFPA defines this as an act of violence committed using digital media and communications technologies against a person on the basis of their gender. Other examples also fall into the category of cybercrimes, such as cyberstalking, doxxing, and revenge porn.
What the discussions revealed was that there remained gaps at the legislative level to address violence against women in online spaces, especially for women in politics. Gender inequality in politics persisted within communities that perpetuated gender inequality on a societal level. When it came to how technology factored into this, it was identified that this would develop at a faster rate than legislation could keep up to address it. Nevertheless, it was important to revisit the legislation and ensure that it could protect all vulnerable communities.
“As parliamentarians, we are perfectly poised, perfectly placed, to ensure this legislation is in place,” Alando Terrelonge, MP, Jamaica, said as the session reached its conclusion. “We have a duty of care to ourselves, as well as a duty of care to women, children, and other vulnerable groups, to ensure that appropriate legislation is in place all over the world and is enacted.”
IPS UN Bureau Report