
Civil Society, Crime & Justice, Democracy, Education, Featured, Global, Globalisation, Headlines, Human Rights, Inequity, Migration & Refugees, TerraViva United Nations
– When all is said and done, it appears that Thomas Hobbes, the 17th century English philosopher who had a dire vision of man, was not totally wrong.
From the frivolous to the serious, in just a week we have had four items of news which would not happen in a normal world. An English porn beauty with 86,000 followers on social media has put bottles of the water she bathes in on sale at 30 pounds a bottle and has sold several thousand bottles.

Roberto Savio
A survey in Brazil found out that 7% of citizens believe that the earth is flat (40 percent of American schools teach that the world was created in a week, according to the Bible, so there cannot be ancient civilisations) Another survey, this time of members of the British Tory party, who seem likely to elect Boris Johnson as prime minister (not exactly a triumph of reason) are so in favour of a “hard” Brexit that they do not care if this means the exit of Scotland and the end of the United Kingdom. Finally, in order to win election, US president Donald Trump has made racism one of his banners and, in a country of immigrants, this has given him an increase of 5 points in opinion polls.
There are so many signs of barbarisation that they would fill a book… and, as Euripides famously wrote: Whom the gods would destroy, they first make mad.
It is not a popular task, but we have to look at the reality and observe that, in the most scientifically and technologically developed period of history, we are living in times of precipitous barbarisation.
Social inequality has become the basis for the new economy. People have now lowered their expectations and are prepared to work part-time in a precarious job, where young people (according to the International Labour Organisation) can hope for a retirement pension of 600 euro a month. This has been accepted by the political system. We even have a study from Spain according to which, in the present housing market, nearly 87% of people need 90% of their salary just to rent a house.
Today, for many, a salary means survival, not a dignified life. The new economy has developed the so-called gig economy: you work to distribute food, but you are a co-entrepreneur without any of the rights of an employee, for an amount that will never allow you to marry. Children have grown accustomed to look at phenomena such as poverty or war as natural. And now politics are not based on ideas but on how you can successfully exploit the guts of the people, waving banners against immigrants (when we are witnessing a rapid fall in the birth rate) and splintering countries between ”We” who represent the people and “You” enemy of the country. The United States is the best example, where Republicans consider Democrats enemies of the United States. And this brings us to a central question: have Trump, Italy’s Matteo Salvini, Brazil’s Jair Bolsonaro and company not been elected democratically? And they are the symptom or the cause of the “populocracy” which is replacing democracy?
It is not possible to offer a sociological or historical study here. Let us just use a bite: we have gone from the Gutenberg era into a new era – the Zuckerberg era.
Those who greeted the arrival of the Internet with enthusiasm also did so because it would democratise communication and therefore bring about greater participation. The hope was to see a world where horizontal communication would replace the vertical system of information which Gutenberg made possible. Information was, in fact, a support for states and business that used it to reach citizens, who had no recourse to feedback. With Internet, people could now speak directly throughout the world and the propaganda which accompanied its arrival was not considered relevant: it is not important to know, it is important to know where to find It. Well, we have all the statistics on how Internet has affected the general level of culture and dialogue.
The attention span of people has declined dramatically. The majority of Internet users do not stay on an item more than 15 seconds. In the last five years, book volumes have been shortened by 29 pages. Today, articles longer than 650 words are not accepted by columnists’ services. The last meeting of editors of international news agencies decided to lower the level of news from the level of 22 years to that of 17 years. In Europe, the percentage of people who buy at least one book a year now stands at 22% (in the United States it is now 10.5%). According to a recent study in Italy, only 40% of the population is able to read and understand a book. In the same country, 13% of libraries have closed in the last ten years. A very popular transmission in Spain was ”59 seconds” which saw a number of people debate round a table; at the 59th seconds their microphones would disappear. Today, the dream of a TV interviewer is that the person interviewed will give a shorter answer than the question. Newspapers are for people over forty. And there is a unanimous complaint about the level of students entering the university: not all are free from mistakes of orthography and syntax. And the list could continue practically ad infinitum.
The problem of barbarisation has major relevance for political participation. The Gutenberg generations were accustomed to dialogue and discussion. Today, 83% of Internet users (80% under the age of 21), do so only in the virtual world they carved out for themselves. People of Group A gather only with people of Group A. If they come across somebody from Group B, they insult each other. Politicians have been able to adjust rapidly to the system. The best example is Trump. All US newspapers together have a circulation of 60 million copies (ten million those of quality, both conservative and progressive). Trump has 60 million followers who take Trump’s tweets as information. The do not buy newspapers, and if they watch TV it is Fox, which is Trump’s amplifier. No wonder that over 80% of Trump’s voters would vote for him again. And the media, which have lost the ability to offer analysis and cover processes, not just events, take the easy path. Let us follow famous people and make the famous more famous. Analytical journalism is disappearing. In the United States it exists thanks to grants … in every European country, there are few quality papers left, and the largest circulation goes to tabloids which spare their readers the effort of thinking. The Daily Mirror in Britain and Bild in Germany are the best examples.
Internet has made everybody a communicator. This is a fantastic achievement. But in this increasing barbarisation, people also use the Internet for transmitting false information, stories based on fantasy, without any of the quality controls that the media world used to have. And artificial intelligence has been taking over, creating many false accounts, which now interfere in the electoral process, as was proven in the last US elections. We have to add to this that the algorithms used by the owners of the Internet aim to trap the attention of users in order to keep them as much as possible. This month, El Pais published a long study entitled “The toxic effects of YouTube”, where it shows how its algorithms push the viewer to items that are of fantasy, pseudoscientific and of great attraction.
This is due to the fact that the owners have become fabulously rich by transforming citizens into consumers. They find out our identity, and they sell it to companies for their marketing, and also for elections. Those owners have unprecedented wealth, never achieved in the real world: not only in that of production, but even in the world of finance, which has become a casino with no control. The entire world of production of services and goods, man-made, is now close to a trillion dollars a day; that same day, financial flows reach 40 trillion dollars. Jeff Bezos ‘s divorce gave his wife 38 billion dollars. That is equal to the annual average income of 20,000 dollars of 19 million people. No wonder that 80 individuals now possess the same wealth as 2.3 billion people (in 2008, they were 1,200 individuals).
According to historians, greed and fear are great engines of change in history. That was also true in the Gutenberg era. But now, they have triggered a combination of both in a short period of time. After the fall of the Berlin Wall, the doctrine of liberal globalisation arrived with such strength that Margaret Thatcher (who with Ronald Reagan ushered in the new vision of individual profits and elimination of social goods) famously talked of TINA: There Is No Alternative.
The entire political system, including Social Democrats, accepted riding a system of values based on greed and unfettered competition at individual level, at state level and at international level. It took twenty years to understand that the poor have become poorer, and the rich richer, and that states have lost much of their sovereignty to multinational corporations and the world of finance. It is worth noting that, in 2009, in order to save a corrupt and inefficient financial system, the world spent 12 trillion dollars (the United States alone, 4 trillion). Since that rescue, banks have paid the impressive amount of 800 billion dollars in penalties for illicit activities.
The financial crisis of 2009 has triggered a wave of fear. Let us not forget that until 2009, there were no sovereignist, populist, xenophobic parties anywhere, except for Le Pen in France. Soon old traps such as “in name of the nation” and “the defence of religion” were resurrected by politicians able to ride fear. A new scapegoat – immigrants – was found and populocrats are now undermining democracy everywhere.
Populocracy is the new wave. Former Italian prime minister Silvio Berlusconi ushered in a new language, and that language has now been updated by Salvini, Trump and so on. Twitter, Facebook and Instagram are the new medium and now the medium is the message. The old elite had not found a new language.
The Zuckerberg era is an era of greed and fear. Zuckerberg is now attempting to create a global currency, the Libra, to be used by his 2.3 billion users. Until now, states were the only entities able to emit money, a symbol of the nation. Zuckerberg’s currency is based entirely on the Internet and will have no control or regulations. In case of a default, we will have a world crisis without precedent. In the Gutenberg era, this was not possible.
But who has made able Jeff Bezos to give 38 billion dollars to a former wife? Who has elected Trump and Salvini and company, who speak on behalf of the nation and the people, and turn those who do not agree into enemies of the nation and the people, creating an unprecedented polarisation, accompanied by an orgy of revolt against science and knowledge, which have supported the elite, and must now be put aside for the good of people.
This process of barbarisation should not obscure an old proverb: every country has the government it deserves. It is called democracy. However, the traditional elite has no code of communication with the new era. The answer will come from citizen mobilization.
A young Swedish girl, Greta Thunberg, has done more with her stubbornness to raise awareness about impending climate change than the entire political system. Even Trump (albeit for electoral reasons) has now declared that climate change is important.
Today, there many “points of light“ appearing in the world. The elections in Istanbul are a good example, as are the mobilisation in Hong Kong, Sudan and Nicaragua, among many others. Let us hope we will reach a point where people will take the reins of the process and awake the world from the precipitous course of barbarisation. Even Thomas Hobbes concluded that humankind will always, soon or later, find the right path, and give itself good governance. He thought that an elite would always be able to lead the masses.
Well, elites are now the Greta Thunbergs of the world.
Publisher of OtherNews, Italian-Argentine Roberto Savio is an economist, journalist, communication expert, political commentator, activist for social and climate justice and advocate of an anti neoliberal global governance. Director for international relations of the European Center for Peace and Development.. He is co-founder of Inter Press Service (IPS) news agency and its President Emeritus.












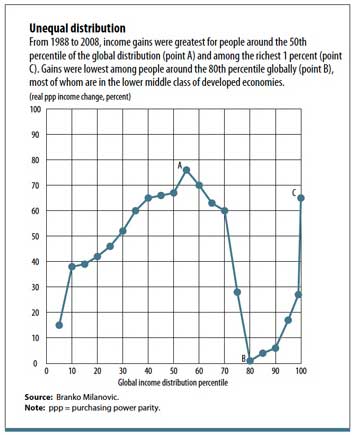 Meanwhile, the lower middle classes in advanced economies saw their earnings stagnate.
Meanwhile, the lower middle classes in advanced economies saw their earnings stagnate.

