Civil Society, Climate Action, Climate Change, Climate Change Finance, Climate Change Justice, COP28, Development & Aid, Editors’ Choice, Environment, Featured, Global, Headlines, Human Rights, Humanitarian Emergencies, Sustainable Development Goals, TerraViva United Nations
Yamide Dagnet, the Director for Climate Justice at Open Society Foundations, delves into the intricacies of the negotiations at the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) 27th session of the Conference of Parties (COP28) in Dubai.

Yamide Dagnet points to the urgency of climate action to meet the Paris Agreements, while protecting frontline communities as about 70 000 attendees grapple with issues during the UN Climate Change Conference COP28. Credit: COP28/Walaa Alshaer
– As the world converges for COP 28, the urgency of addressing climate change has never been more palpable. In an exclusive interview with IPS, Yamide Dagnet, the Director for Climate Justice at Open Society Foundations, delves into the intricate details of this pivotal conference—from the unprecedented start to key challenges and opportunities in climate finance. She offers a comprehensive and nuanced perspective on global climate discourse.
As COP 28 unfolds, this interview provides a panoramic view of the complex landscape of climate action. From the challenges of climate finance to the critical role of the private sector and the ethical considerations in technology deployment, Dagnet offers a roadmap for navigating the intricate terrain of climate change, including an urgent call to action urging global leaders, businesses, and civil society to address the challenges that lie ahead collaboratively. As the world grapples with the consequences of climate change, the interview serves as a compass, guiding stakeholders towards a more sustainable and resilient future, and her voice clearly articulates her views that while the just energy and industrial revolution hold immense potential for economic growth in resource-rich nations, it is crucial to protect the rights of frontline communities and activists.
The Start of COP 28
The conference’s initial day set an unprecedented tone. “Positive developments like the creation of the Loss and Damage Fund and sizeable pledges, especially from countries like the UAE, Germany, and the EU, are highlights of this momentum’s emphasis on international solidarity; I hope that the momentum generated on day one will permeate the entirety of COP 28,” Dagnet told Inter Press Service.

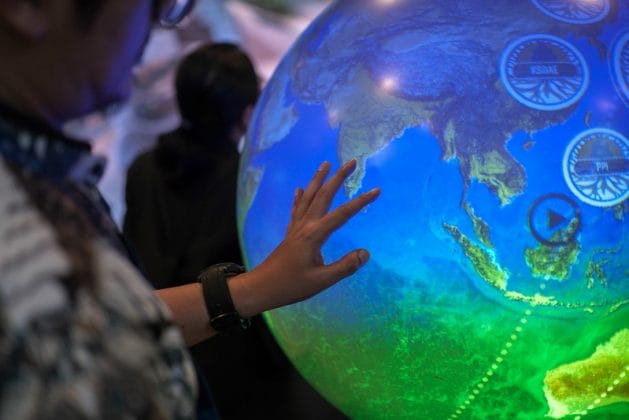
Yamide Dagnet, Director for Climate Justice at Open Society Foundations. Credit: TJ Kirkpatrick, Open Society Foundations
Wealthier Nations and Climate Change
Dagnet delves into the role of wealthier nations in the fight against climate change. “While there is an expectation for these nations to fulfil their commitments, reality paints a different picture. Adaptation finance has not seen the necessary investment,” she said while pointing to a critical gap in addressing the immediate impacts of climate change. Looking at the financial dynamics, Dagnet dissected the pledges made by key nations and highlighted the ongoing challenges in reaching the financial targets made since 2009 and outlined in the Paris Agreement. Dagnet contends that “fulfilling pledges and demonstrating seriousness are essential steps for wealthier nations to regain trust and ensure a unified front in the fight against climate change.”
Key Trends in Climate Change Policy
Transitioning into a discussion on key trends shaping climate change policy in the next decade, Dagnet underscored the critical importance of aligning investments with the goals of the Paris Agreement. A concerning trend emerges as she highlights the “doubling of subsidies for fossil fuels, signaling a misalignment with the imperative to transition to clean energy. There is a need to redirect investments toward clean energy, adaptation, and activities in line with the Paris Agreement.”
Delving into philanthropic organizations’ role in supporting climate action, Dagnet says that while some positive dynamics have emerged on loss and damage, much work remains to be done. “Let us not forget that economic and non-economic losses and damages cost several hundreds of thousands of dollars each year.” She says there is a need to prioritize investments in supporting adaptation efforts, acknowledging the urgent need for resilience in the face of climate change impacts. She is hopeful as diverse group of eleven philanthropic organizations committed on December 2 to develop a joint strategic plan, joining the global chorus of voices calling for increased funding and action on climate adaptation.
Balancing Economic Goals and Climate Policies
Dagnet also highlights the challenge of balancing economic goals while adhering to climate policies, emphasizing the integration of climate policy into the broader development agenda. She illustrated the economic risks posed by climate-related disasters, citing examples of hurricanes causing widespread destruction. “Resilient infrastructure is vital, as even substantial economic gains can be wiped out if development projects are not resilient to floods, hurricanes, and other climate-related events,” she said.
Exploring the business sense of investing in reducing emissions, Dagnet highlights that, with the decreasing costs of renewable energy, it is not only an environmental imperative but also financially prudent. “The cost-effectiveness of renewable energy makes a compelling case for nations to prioritize emission reduction efforts, aligning economic goals with sustainable development,” she said.
It also means recognizing that the rare transition minerals needed to scale up the use of renewable energy require a just energy and industrial revolution, which holds immense potential for economic growth in resource-rich nations.
“However, the risk of human rights abuses and other adverse effects should be taken into account and mitigated by focusing on value addition in mineral supply chains by reconciling with the protection of activists and frontline communities, including people’s rights in land use, labor, and conservation of cultural heritage.”
The Role of the Private Sector
Dagnet further delves into the role of the private sector in climate action, focusing on areas such as adaptation and loss and damage. She acknowledged the challenges faced by the private sector in engaging with these aspects, emphasizing the need for them to integrate climate risk into their business models. “While adaptation may not seem immediately profitable, the long-term consequences of inaction are severe,” she says. She suggests that insurance companies need to review their business models, considering how they can better contribute to tackling losses and damages.
Technology for Addressing Climate Change
Turning to the role of technology in addressing climate change, Dagnet discussed the potential and pitfalls. She advocates for a “balanced approach that leverages indigenous knowledge alongside technological solutions. Dagnet highlights the importance of proper assessment, monitoring, safeguards, and global governance to mitigate the risks associated with less-proven and more controversial solutions like geoengineering, carbon dioxide removal, and carbon capture and storage. This is critical for responsible technology deployment, recognizing that while technology can offer solutions, it must be guided by ethical considerations, an understanding of potential risks, and the design of appropriate guardrails to minimize unintended adverse impacts.” She suggested that a holistic approach, which includes both technological advancements and indigenous knowledge, together with a more participatory process bringing various constituencies from both the global north and global south, provides a more robust foundation for addressing climate change challenges in an innovative and equitable way.
Civil Society’s Accountability Role
Dagnet further highlighted the vital role of civil society in holding governments accountable for their climate commitments, including their financial pledges. She contends that efforts to “measure progress and scrutinize government actions are essential tools for civil society to hold governments accountable for their commitments.” She also acknowledged the power of public pressure to drive governments to take more ambitious climate action. Dagnet emphasized the need for a multi-faceted approach, combining legal frameworks, grassroots movements, and international collaboration based on robust data and supported by nuanced and more sophisticated communication strategies, to hold governments accountable on the global stage effectively.
Assessment of International Agreements
Dagnet provided a sober assessment of the international agreements reached so far in the fight against climate change. She also acknowledged that the world is far from achieving its climate objectives, and the window to meet temperature goals is shrinking rapidly. But like many climate justice avengers, she is not defeated and points out ways COP28 and its global stocktake can create an inflection point, with a “course correction pathway” that highlights the need for increased attention to scaling up efforts to keep global temperature increases to 1.5 degrees Celsius and enhance resilience, especially in the face of recent climate-related disasters globally. “No country is immune to the disasters the climate change is unleashing. It is imperative to scale up and speed up efforts to keep fossil fuels on the ground while focusing on building resilience to mitigate the impact of climate change,” she concluded.
IPS UN Bureau Report