Civil Society, Headlines, TerraViva United Nations
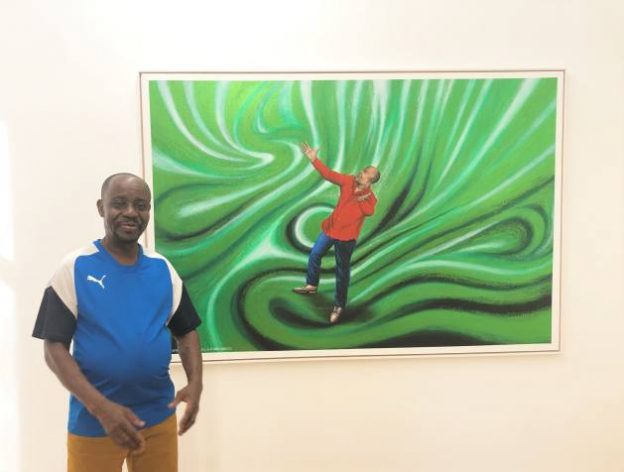

The show “Kings of Kin” – brings together the work of Chéri Samba (pictured above), Bodys Isek Kingelez and Moké, known affectionately as the kings of Kinshasa, as their art is closely linked with the capital of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, their home and work base. Credit: AD McKenzie
– Chéri Samba has a sly sense of humour, both in person and in his work. Standing in front of his 2018 painting “J’aime le jeu de relais” (I Love the Relays) – which criticizes politicians who cling to power instead of passing the baton – Samba is asked about the resemblance of one of his subjects to a famous statesman.
“Oh, I was just portraying a politician in general. I didn’t really have a particular person in mind because they all have certain characteristics,” he responds. Then he adds mischievously, “Isn’t it me though? Doesn’t it look like me?”
In this case it doesn’t, but the Congolese artist sometimes depicts himself in various guises in his paintings. Visitors to the current exhibition in Paris featuring his work and those of two of his equally acclaimed countrymen will have fun trying to spot him on canvas.
The show – Kings of Kin – brings together the work of Samba, Bodys Isek Kingelez and Moké, known affectionately as the kings of Kinshasa, as their art is closely linked with the capital of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, their home and work base. All three have participated in numerous exhibitions around the world, in group and solo shows, but this is the first time they’re being shown together in galleries.
Kings of Kin is being held jointly at the MAGNIN-A and the Natalie Seroussi galleries (running until Oct. 30) and features some 30 works, including Samba’s latest paintings. He is undoubtedly the star attraction with his bold, massive canvases commenting on social and political issues in Africa and elsewhere, but the others command attention as well.
Samba also is the only surviving “king” as Moké died in 2001 and Kingelez in 2015.
On a recent unseasonably hot afternoon, the artist is present at the MAGNIN-A gallery, speaking with a visitor who’s wearing a mask, although he himself is without one. He says he came to Paris in January, then got caught in the lockdown as the Covid-19 pandemic spread in France. He has used the time to complete several paintings for the current show.
Asked if he doesn’t miss the “inspiration” that Kinshasa provides, Samba replies that all artists should be able to produce work wherever they find themselves.
“I live in the world, and I breathe as if I’m in Kinshasa,” he says. “In my head, I want to live where I can speak with people and where they understand me. I travel with the same brain. I would like to be in Kinshasa, but this doesn’t prevent me from creating. The world belongs to all of us.”
His new paintings fill the entry and the main hall of the MAGNIN-A gallery, with bright greens, reds, blues – inviting viewers into his mind or current state of world awareness.
The first work that strikes the eye is “Merci, merci je suis dans la zone verte” (Thank you, thank you I’m in the green zone), which depicts a man – the artist – seemingly caught in a vortex of some sort. Painted this year, the painting reflects the current global upheavals with the Covid-19 and other ills. It could also be referencing the DRC’s past under brutal colonialism and the difficulties of the present.
Another equally compelling work features the faces of six girls of different ethnicities, produced in acrylic with particles of glitter, and titled: “On Est Tout Pareils” (We’re All the Same). Samba says that his daughter served as the model and that the painting is a call for peace, equality and the ability to live together without discord.
The oldest of his paintings on display dates from 1989 and reveals a very different style, with softer colours and intricate workmanship, as he portrays a Congolese singer – the late feminist performer M’Pongo Love – wearing an attractive dress. Here the broad strokes are absent, and the designs on the dress are meticulously captured.
He says that although viewers may notice variations between his earlier output and the new works, he tends not to take note of such differences.
“All the paintings are like my children,” he says. “I can’t make distinctions between them.”
In contrast to Samba, the paintings by Moké comprise softer hues and have a more earthy feel, but they also compel the viewer to see into the lives of those depicted. Moké’s subjects nearly always elicit a certain empathy, a certain melancholy, and sometimes hope – whether these subjects are performers or an older couple simply having dinner together.
Moké lived for only 51 years, but his output was impressive – dating from the time he arrived in Kinshasa as a child and began painting urban landscapes on cardboard. He considered himself a “painter-journalist” and portrayed the everyday life of the capital, including political happenings. One of his paintings from 1965 depicts then-general Mobutu Sese Seko waving to the crowds as he came to power in Zaire (the previous name of the DRC).
In the Paris show, Moké’s paintings depict boxers, performers, frenetic city scenes, and portraits of women staring out with expressions that are both bold and solemn.
Meanwhile, the work of Kingelez takes viewers into a sphere of colourful towers and other “weird and wonderful” structures with a utopian bent, as he imagines a world that might possibly rise from the ravages of colonialism, inequity and bad urban planning.
The first Congolese artist to have a retrospective exhibition at New York’s Museum of Modern Art (“City Dreams” in 2018), Kingelez used everyday objects such as paper, cardboard and plastic to produce his first individual sculptures before creating whole fantastical cities.
His futuristic urban settings, which also address social issues, thus form a perfect companion to the “surreal earthliness” of Samba and Moké in Kings of Kin.
“These are artists who worked because of deep necessity, because they had something to say. It wasn’t about the art market or commerce,” said French gallery owner and independent curator André Magnin, who first encountered their work in the 1980s in Kinshasa.
The author of several books on Congolese art, Magnin said he hoped visitors to the exhibition would discover the unique “artistic richness” of the Congo region as exemplified by the “kings”. As for “queens”, he said that there weren’t many women artists working at the time, but that more are now becoming known and should be the focus of coming shows.
Dorine, a French art student of African descent who visited the exhibition, said she admired the artists and particularly Samba because he “speaks of African reality”.
“Their work is very interesting, and the message is extremely strong,” she told SWAN.