Biodiversity, Civil Society, Conservation, Development & Aid, Economy & Trade, Editors’ Choice, Energy, Environment, Featured, Food and Agriculture, Headlines, Integration and Development Brazilian-style, Latin America & the Caribbean, Natural Resources, Projects, Regional Categories, TerraViva United Nations, Water & Sanitation

Residents of the municipality of Castro, in Chiloé, an archipelago in southern Chile, demonstrate in the streets of their city, in front of the Gamboa Bridge, expressing their fear of threats to the water supply that they attribute to the lack of protection of peatlands, which are key to supplying water for the island’s rivers. CREDIT: Courtesy of Chiloé en defensa del Agua
– The drinking water supply in the southern island of Chiloé, one of Chile’s rainiest areas, is threatened by damage to its peatlands, affected by sales of peat and by a series of electricity projects, especially wind farms.
The peat bog (Moss sphagnum magellanicum) known as “pompon” in Chile absorbs and retains a great deal of water, releasing it drop by drop when there is no rain. In southern Chile there are about 3.1 million hectares of peatlands.
“We condemn the fact that the extraction of peat is permitted in Chiloé when there is no scientifically proven way for peat to be reproduced or planted…. there is no evidence of how it can regenerate.” ¨– Daniela Gumucio
Peat is a mixture of plant debris or dead organic matter, in varying degrees of decomposition, neither mineral nor fossilized, that has accumulated under waterlogged conditions.
The pompon is the main source of water for the short rivers in Chiloé, an archipelago of 9181 square kilometers and 168,000 inhabitants, located 1200 kilometers south of Santiago. The local population makes a living from agriculture, livestock, forestry, fishing and tourism, in that order.
“We don’t have glaciers, or thaws. Our water system is totally different from that of the entire continent and the rest of Chile. Since we don’t have glaciers or snow, our rivers function on the basis of rain and peat bogs that retain water and in times of scarcity release it,” Daniela Gumucio told IPS by telephone.
The 36-year-old history and geography teacher said that the Chiloé community is concerned about the supply of drinking water for consumption and for small family subsistence farming.
Gumucio is a leader of the National Association of Rural and Indigenous Women (Anamuri) and chairs the Environmental Committee of Chonchi, the municipality where she lives in the center of the island.
This long narrow South American country, which stretches between the Andes Mountains and the Pacific Ocean, has 19.5 million inhabitants and is facing one of the worst droughts in its history.
It’s strange to talk about water scarcity in Chiloé because it has a rainy climate. In 2011 more than 3000 millimeters of water fell there, but since 2015 rainfall began to decline.
In 2015 rainfall totaled 2483 millimeters, but by 2023 the amount had dropped to 1598 and so far this year only 316, according to data from the Quellón station reported to IPS by the Chilean Meteorological Directorate.
The forecast for April, May, and June 2024 is that below-normal rainfall will continue.
A water emergency was declared in the region in January and the residents of nine municipalities are supplied by water trucks.
To supply water to the inhabitants of the 10 municipalities of Chiloé, the State spent 1.12 million dollars to hire water trucks between 2019 and 2024. In Ancud alone, one of the municipalities, the expenditure was 345,000 dollars in that period.
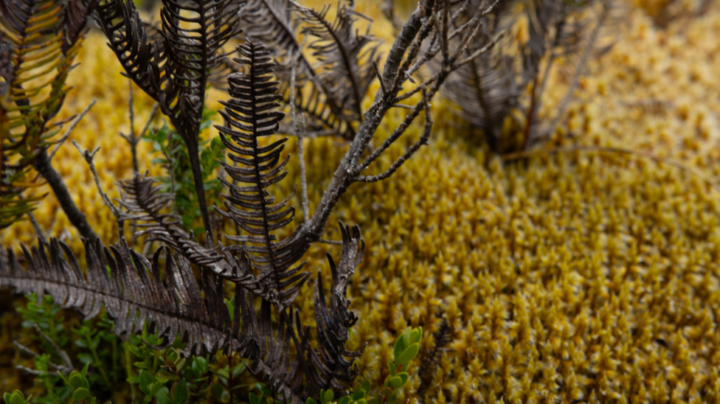

A close-up shot of a peat bog in a watershed on the island of Chiloé, which has the ability to absorb water 10 times its weight. Because of this property, those who extract it today, without any oversight, dry it, crush it and pack it in sacks to sell it to traders who export it or sell it in local gardening shops. CREDIT: Courtesy of Gaspar Espinoza
Alert among social activists
The concern among the people of Chiloé over their water supply comes from the major boost for wind energy projects installed on the peat bogs and new legislation that prohibits the extraction of peat, but opens the doors to its use by those who present sustainable management plans.
Several energy projects are located in the Piuchén mountain range, in the west of Chiloé, where peat bogs are abundant.
“They want to extend a high voltage line from Castro to Chonchi. And there are two very large wind farm projects. But to install the turbines they have to dynamite the peat bog. This is a direct attack on our water resource and on our ways of obtaining water,” Gumucio said.
In 2020, the French company Engie bought three wind farms in Chiloé for 77 million dollars: San Pedro 1 and San Pedro 2, with a total of 31 wind turbines that will produce 101 megawatts (MW), and a third wind farm that will produce an additional 151 MW.
In addition, 18 kilometers of lines will be installed to carry energy to a substation in Gamboa Alto, in the municipality of Castro, and from there to the national power grid.
Another 92 turbines are included in the Tabla Ruca project, between the municipalities of Chonchi and Quellón.
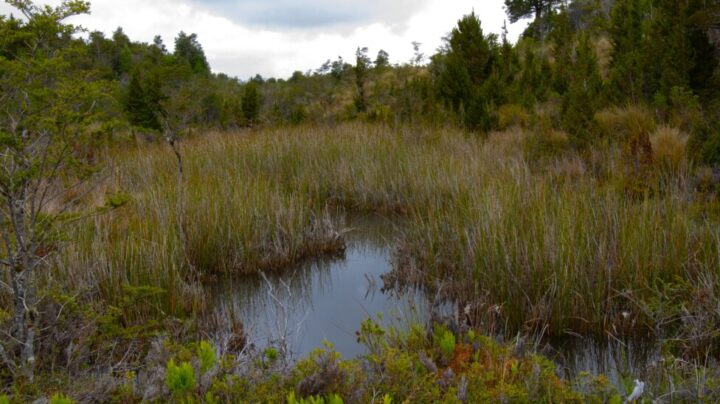

Peat bogs accumulate and retain rainwater in the wetlands of Chiloé and release it drop by drop to river beds in times of drought. CREDIT: Courtesy of Gaspar Espinoza
Engie describes its initiatives as part of the transition to a world with zero net greenhouse gas emissions, thanks to the production of clean or green energy.
Leaders of 14 social and community organizations expressed their concerns in meetings with regional authorities, but to no avail. Now they have informed their communities and called on the region’s authorities to protect their main water source.
Local residents marched in protest on Mar. 22 in Ancud and demonstrated on Apr. 22 in Puente Gamboa, in Castro, the main municipality of the archipelago.
Thanks to peatlands, the rivers of Chiloé do not dry up. The peat bogs accumulate rainwater on the surface, horizontally, and begin to release it slowly when rainfall is scarce.
For the same reason, peat is dup up and sold for gardening. In 2019 Chile exported 4600 tons of peat.
The wind energy projects are set up in areas of raised peat bogs, known as ombrotophic, located at the origin of the hydrographic basins.
“We have had a good response in the municipal council of Chonchi, where the mayor and councilors publicly expressed their opposition to approving these projects,” said Gumucio.
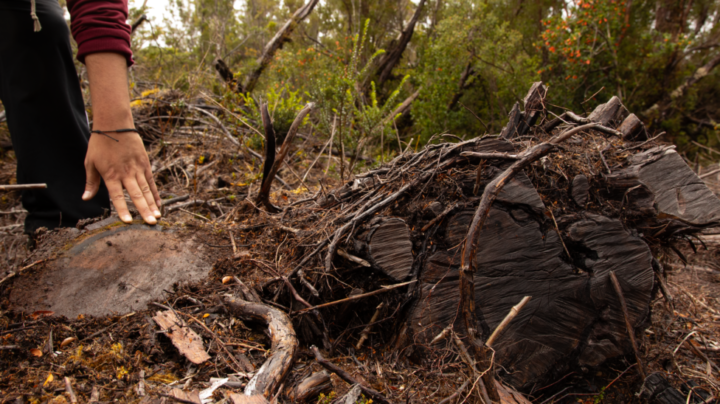

Dozens of trees have been felled in Chiloé to install wind turbines and make way for high-voltage towers that will transmit green energy to Chile’s national power grid, without benefiting the inhabitants of the Chiloé archipelago. CREDIT: Courtesy of Gaspar Espinoza
The other threat to peatlands
The second threat to the Chiloé peat bogs comes from Law 21.660 on environmental protection of peatlands, published in Chile’s Official Gazette on Apr. 10.
This law prohibits the extraction of peat in the entire territory, but also establishes rules to authorize its use if sustainable management plans are presented and approved by the Agricultural and Livestock Service, depending on a favorable report from the new Biodiversity and Protected Areas Service.
The peatland management plan aims to avoid the permanent alteration of its structure and functions.
Those requesting permits must prove that they have the necessary skills to monitor the regeneration process of the vegetation layer and comply with the harvesting methodology outlined for sustainable use.
But local residents doubt the government’s oversight and enforcement capacity

Dozens of trees have been felled in Chiloé to install wind turbines and make way for high-voltage towers that will transmit green energy to Chile’s national power grid, without benefiting the inhabitants of the Chiloé archipelago. CREDIT: Courtesy of Gaspar Espinoza
“We condemn the fact that the extraction of peat is permitted in Chiloé when there is no scientifically proven way for peat to be reproduced or planted…. there is no evidence of how it can regenerate,” said Gumucio.
The activist does not believe that sustainable management is viable and complained that the government did not accept a petition for the law to not be applied in Chiloé.
“We have a different water system and if this law is to be implemented, it should be on the mainland where there are other sources of water,” she said.
But according to Gumucio, everything seems to be aligned to deepen the water crisis in Chiloé.
“The logging of the forest, the extraction of peat, and the installation of energy projects all contribute to the drying up of our aquifers and basins. And in that sense, there is tremendous neglect by the State, which is not looking after our welfare and our right to have water,” she argued.
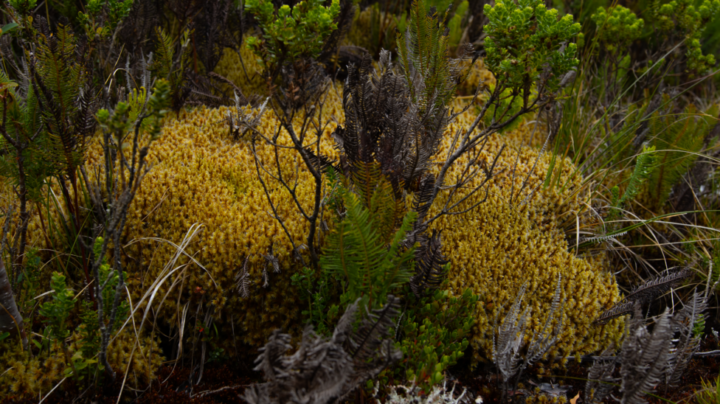

Peatland is part of the vegetation of the island of Chiloé, but is threatened by unsupervised exploitation, which the authorities hope to curb with a recently approved law, whose regulations are to be ready within the next two years. CREDIT: Courtesy of Gaspar Espinoza
Scientists express their view
Six scientists from various Chilean universities issued a public statement asserting that the new law is a step in the right direction to protect Chile’s peatlands.
In their statement, scientists Carolina León, Jorge Pérez Quezada, Roy Mackenzie, María Paz Martínez, Pablo Marquet and Verónica Delgado emphasize that the new law “will require the presentation of a sustainable management plan” to exploit peat that is currently extracted without any controls.
They add that management plans must now be approved by the competent authorities and that those who extract peat will be asked to “ensure that the structure and functions of the peatlands are not permanently modified.”
They also say that the regulations of the law, which are to be issued within two years, “must establish the form of peat harvesting and post-harvest monitoring of the peat bog to protect the regeneration of the plant, something that has not been taken into consideration until now.”
They point out that the new law will improve oversight because it allows monitoring of intermediaries and exporters who could be fined if they do not comply with the legislation.
“While it is true that there is concern among certain communities and environmental groups, we believe that these concerns can be taken into account during the discussion of the regulations,” they say.
The scientists reiterate, however, that “peatlands are key ecosystems for mitigating the national and planetary climate and biodiversity crisis” and admit that “significant challenges remain to protect them, although this is a big step in the right direction.”