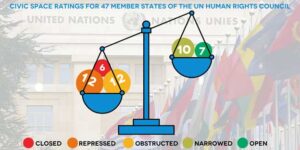
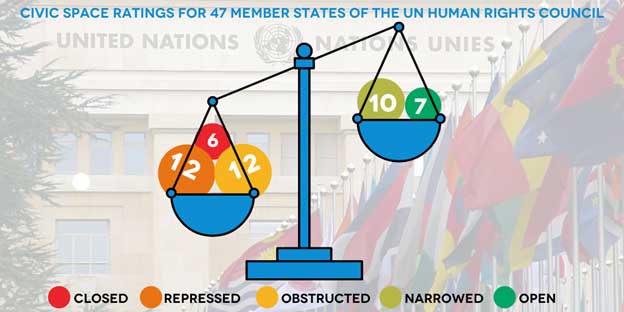
Civil Society, Democracy, Editors’ Choice, Featured, Headlines, Human Rights, Indigenous Rights, Latin America & the Caribbean, Regional Categories, TerraViva United Nations
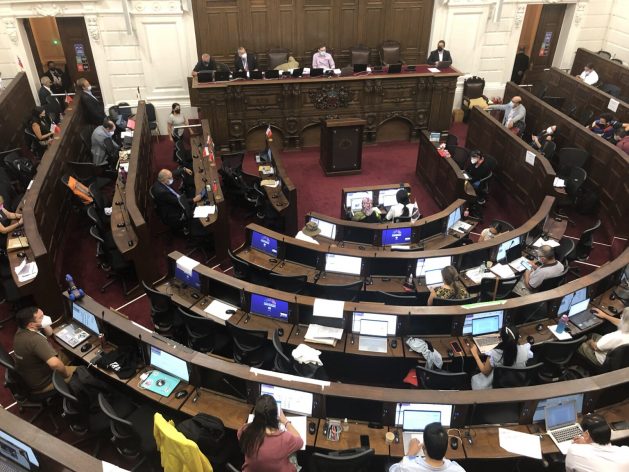

A Mar. 3 plenary session of the constitutional convention of Chile, where in long working days its members are drafting a new constitution, which must be completed by Jul. 4 at the latest. On Feb. 17, they approved by a large majority the new definition of Chile as a regional, plurinational and pluricultural State. CREDIT: Orlando Milesi/IPS
– Chile could change the course of its history and become a diverse and multicolored country this year with a “plurinational and intercultural state” that recognizes and promotes the development of the native peoples that inhabited this territory before the Spanish conquest.
By 112 votes in favor and 32 against, the constitutional convention approved this proposal which now forms part of the draft constitution that Chilean voters will approve or reject in an August or September referendum.
“The current Chilean constitution and the previous ones make no mention of the words Indian, native…indigenous peoples, or original peoples. Nothing. They are erased from the constitution because they were made invisible socially, culturally, economically, politically and militarily.” — Domingo Namuncura
The constitutional convention is debating and drafting a new constitution which is the result of the work of 155 constituents – half men and half women, with 17 indigenous members – elected by popular vote in October 2020 who began the task on Jul. 4, 2021. They have until Jul. 4 to finish their work.
In the country’s last census, in 2017, 2.18 million Chileans self-identified as indigenous people.
In other words, 12.8 percent of the 17.07 million inhabitants of Chile at that time (today the population stands at 19.4 million) were recognized as belonging to one of the indigenous peoples distributed throughout this long narrow South American country: the Mapuche (the largest native group), followed by the Aymara, Rapa Nui, Diaguita, Atacameño, Quechua, Colla, Kawesqar and Yagan.
Domingo Namuncura, a Mapuche social worker and professor at the Catholic University of Valparaíso, told IPS that “we are facing a very important historic event. The declaration of a plurinational State has always been a dream of the indigenous peoples of Chile.”
The creation of the constitutional convention was the response to months of protests and social unrest in 2019, the repression of which tainted the second term of right-wing President Sebastián Piñera, a businessman who had already governed the country between 2010 and 2014, and who will be succeeded as of Mar. 11 by the leftist Gabriel Boric, winner of the December elections.
Chile has been governed since 1980 by the constitution imposed by the dictatorship of General Augusto Pinochet (1973-1990), who used legislation to put in place a neoliberal and authoritarian economic and political regime, which democratic governments have only been able to partially dismantle since 1990.
The result is a country with a dynamic economy based on exports of mining and agricultural products, but with one of the most unequal societies in the world, which was at the basis of the 2019 demonstrations, as was the failure to fulfill promises of change, such as a new constitution, the reform of the educational system or improvements in social rights.
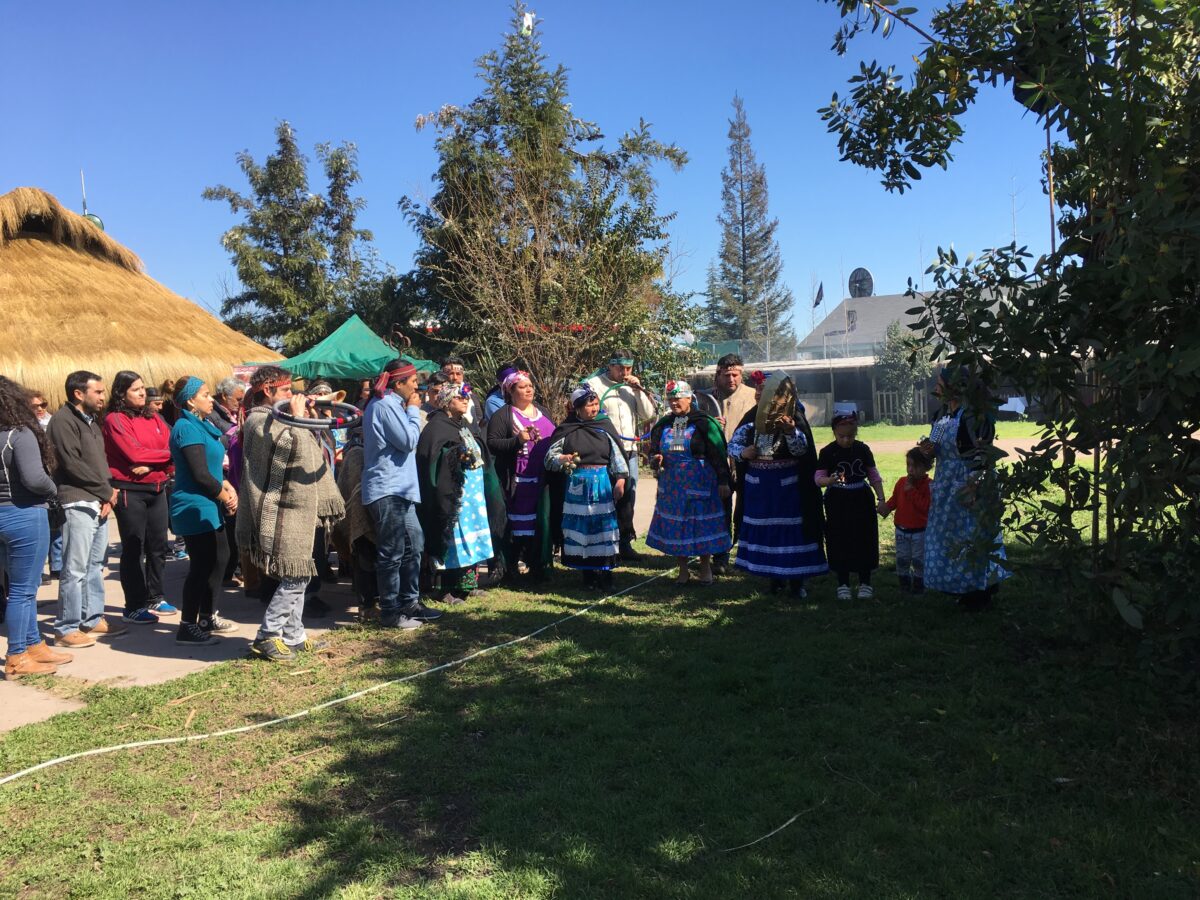

Mapuche Indians living in the metropolitan region. Data from 2021 indicate that the Mapuche, Chile’s largest indigenous people, number 1.8 million, followed by the Aymara (156,000) and the Diaguita (88,000). CREDIT: Orlando Milesi/IPS
Arguments of the constituents
No previous Chilean constitution has mentioned indigenous people and their rights, by contrast with other Latin American constitutions that have emerged since 1980. And the only precedent of declaring a “plurinational state” is that of neighboring Bolivia, which did so in its 2009 constitution.
“The current Chilean constitution and the previous ones make no mention of the words Indian, native…indigenous peoples, or original peoples. Nothing. They are erased from the constitution because they were made invisible socially, culturally, economically, politically and militarily,” said Namuncura.
Adolfo Millabur, Chile’s first Mapuche mayor, elected in 1996 in the southern town of Tirúa, resigned from his post to become a member of the constitutional convention, to occupy one of the seats reserved for Mapuche representatives. He maintained that “if Chile is transformed and defines itself as a plurinational state, what changes is its democratic vocation.”
“By acknowledging the peoples that lived here prior to the creation of the Chilean State, a collective actor is given value. Different forms of relations should begin to be established, especially in the area of political definition and participation,” he told IPS.
Lawyer Tiare Aguilera, a member of the constitutional convention from the Rapa Nui people, believes that “the most important thing is to reach the referendum with a citizenry that is informed about plurinationality and its implications.”
In her view, “through plurinationality, our country will finally be able to advance towards reparations for the native peoples of Chile.
“There is a great deal of ignorance among the public. If we correctly inform and educate the public about their meanings and implications, we believe that the changes in the definition of the State will be understood,” she told IPS.

The facade of the old National Congress, where since July 2021 the members of the constitutional convention have been debating the new form of State that will govern Chile starting this year, if the draft constition is approved in a referendum. CREDIT: Orlando Milesi/IPS
Jaime Bassa, a member of the constitutional convention who was its vice-president until January, said “the normative proposals approved in commissions and in the plenary on plurinationality speak to us of a sense of reality, of accepting ourselves in legitimate diversity and coexistence, of recognizing our historical roots, of valuing ourselves based on our cultural identity.
“In comparative experiences, plurinationalism and multilingualism have brought about interesting cultural changes that have led to innovative and sustainable development alternatives,” he told IPS.
In his opinion, “the growth and development model we are moving towards within the framework of the constituent process that is underway should promote ethics and inter-territorial solidarity, care for the environment and sustainability, as foundations for political equality, and to ensure collaborative, resilient contexts of respect for rights that allow us to broaden and deepen our democracy.”
Bassa said the constitutional convention “is working on a proposal for a plurinational and decentralized legislative power in which there is equality, which would give rise to representation for the different territories, that would participate in the process of law-making, effectively representing the peoples and nations that coexist within the State.”
The regulation approved on Feb. 17 states that “Chile is a regional, plurinational and intercultural State made up of autonomous territorial entities, within a framework of equity and solidarity among all of them, preserving the unity and integrity of the State.”
According to Namuncura, who was the first Mapuche to serve as a Chilean ambassador, to Guatemala, “Chile has always been plurinational because it is constituted on the basis of different native populations that were already in this territory and that joined as native peoples or nations, by force or otherwise, in the construction of the national State.
“From the Aztec, Mayan, Inca and Mapuche cultures, before the arrival of the Spaniards, America was already a plurinational continent populated by more than 1,200 indigenous nationalities that were formed many centuries ago,” he pointed out.
The convention is also discussing other norms for indigenous peoples, such as their own courts of justice in coordination with the national justice system, a parliament with indigenous representation and a regime governing natural resources located in their territories.
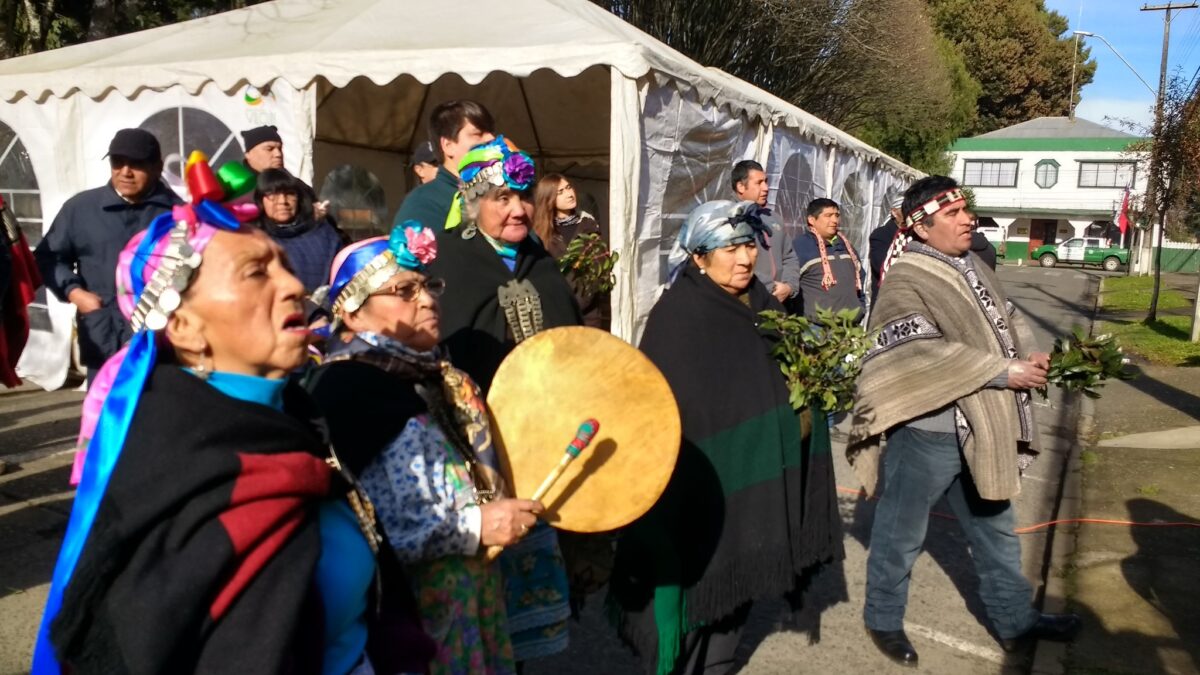

Representatives of the Mapuche, Lonko and Machi peoples take part in the raising of the flag in the Plaza de Armas in Vilcún, 700 km south of Santiago, in one of the many events held in Chile every Jun. 24, declared a national holiday for We Tripantu (new sunrise), the Mapuche New Year. CREDIT: Mirna Concha/IPS
Business leaders unhappy
This process is of great concern to the business leaders grouped in the Confederation of Production and Commerce (CPC), whose board, headed by Juan Sutil, met several times with Mapuche representative Elisa Loncón, who was president of the convention until January, and her successor, María Elisa Quinteros.
The CPC was behind numerous Popular Standards Initiatives seeking to include its positions in the debate. It invited everyone to support these initiatives “that defend the values of freedom of thought and free enterprise,” among others, in order to achieve “a robust democracy” with public-private collaboration.
The CPC gathered 507,852 signatures and was able to submit 16 initiatives with its views on the constituent process. Three of them have already been rejected: “Free enterprise”, “Economic model, freedom of entrepreneurship and promotion of small and medium-sized enterprises”, and “Water for all”. One more is still being processed: “Towards sustainable mining for Chile”.
Business leaders have raised the tone of their opposition to the convention, which they accuse of distancing itself from the real Chile and from the work for a constitution for all.
“I am concerned that the constitution that is being drafted is not generating the proper balances and will not be a constitution that takes into account the sensibilities of all Chileans,” said Sutil.
Those sensitivities, he said, are especially from “a minority sector, which could be the center right, the right and even people from the center within the convention itself who are not being taken into consideration at all,” he told a local radio station.
“Chile is much more than what the constitutional convention reflects. The correlation of forces is very different in the real Chile than what is happening in the convention,” he argued.
According to Sutil, criticism of the convention is widespread and “this is bad not only because it jeopardizes the process, but also because it jeopardizes the future of the country from an institutional point of view, and from the point of view of its development and growth.”
Forestry companies own approximately 1.9 million hectares in an enormous area in the south, across three of the country’s regions. A significant part of these hectares are the ancestral lands of indigenous peoples.
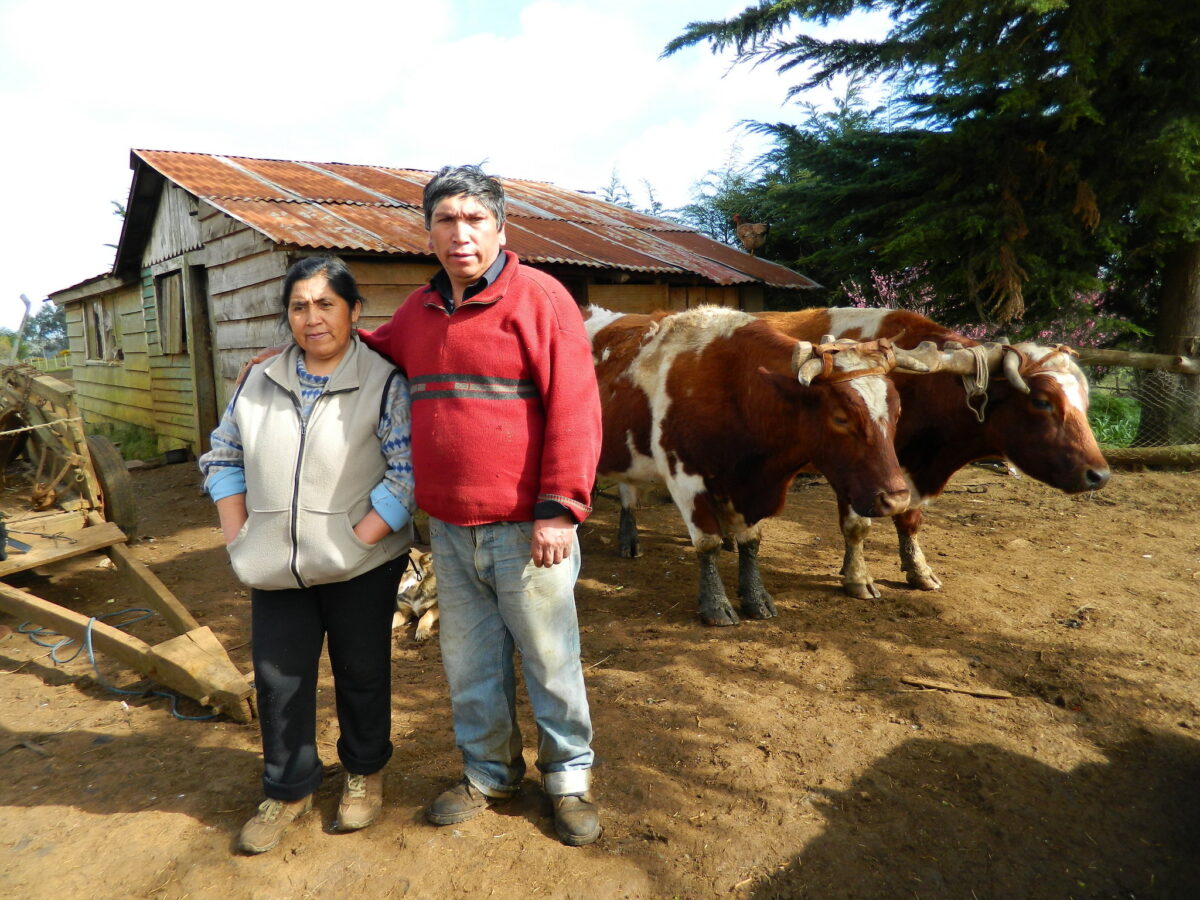

Catalina Marileo and Luis Aillapán, a Mapuche couple, stand in front of their home in Puerto Saavedra in the central Chilean region of La Araucanía. They have been among the many members of native peoples tried under an anti-terrorism law inherited from the dictatorship for acts such as, in their case, opposing the military for building a road on their land. Now Chile could be declared a plurinational State. CREDIT: Marianela Jarroud/IPS
Precedents of a truth commission
The Historical Truth and New Deal with Indigenous Peoples Commission, created by then president Ricardo Lagos in 2001 and composed of 24 members with cross-cutting representation, found that 500,000 hectares were awarded to indigenous peoples between 1884 and 1929. This was verified after reviewing 413 titles issued in that time span.
The purpose of the Commission was to “correct the historical invisibility of native peoples, recognize their identity, repair the damage done to them and contribute to the preservation of their culture.”
In its final report, in 2003, the Commission proposed a hundred measures. In the area of land, it called for protecting lands belonging to indigenous peoples, demarcating and titling ancestral lands of native communities, and establishing a land reclamation mechanism.
Regarding natural resources, it proposed recognizing the indigenous peoples’ right of ownership, use, administration and benefit, the preferential right in State concessions, and the right of use, management and conservation.
So far, the greatest gesture by the State for the mistreatment of indigenous peoples was made by the current United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights Michelle Bachelet, who as president of Chile (2006-2010 and 2014-2018) apologized in June 2017 to the Mapuche in a solemn official act for “the errors and horrors” committed against them.
Namuncura believes that a pending task is “to reach a political agreement with the large forestry companies so that a part of these lands, which today are their property, are returned to the indigenous peoples through a long-term political and financial commitment, with the possibility of considering the value of this restitution.”
The wording already approved for the first draft will now be analyzed by the Harmonization Commission, which will ensure “the concordance and coherence of the constitutional norms approved by the plenary.”
The version that emerges from that process will be voted by the plenary which, by two thirds, will define the text to be voted on by all Chileans in the referendum.