Armed Conflicts, Civil Society, Editors’ Choice, Europe, Featured, Headlines, Human Rights, Humanitarian Emergencies, International Justice, Peace, TerraViva United Nations
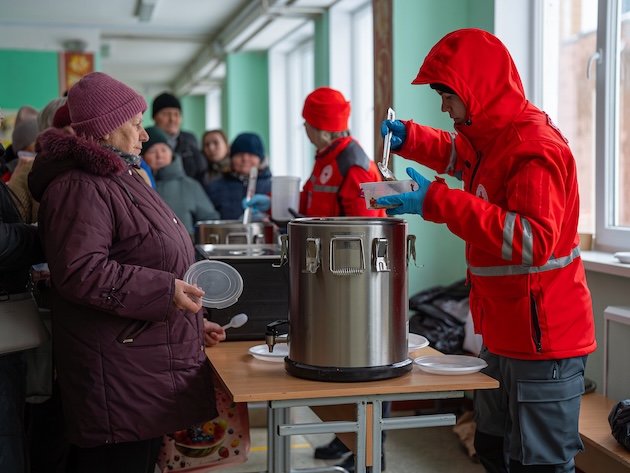

Ukrainian Red Cross teams have delivered over 3,300 hot meals to Kyiv residents at support points around the city. Credit: Red Cross
– “We have a saying here in Ukraine now – ‘young people meet at their friends’ funerals rather than at weddings.’ It’s sad, but very true.”
As Russia’s full-scale invasion of her country moves into its fifth year, Iryna Yakova, 29, is looking back at how her life has changed over the past four years.
Speaking from Lviv, the western Ukrainian city where she lives, she tells IPS that her “values and attitude towards life” have changed. “Material things become unimportant when your loved ones or friends are in danger,” she says. She has also developed a keen sense of her national identity and an empathy for the suffering of her fellow Ukrainians.
“During the full-scale invasion, I realised that all of Ukraine is my home. I cry for people who were killed by a missile in Kyiv while they were sleeping at night. Even though I didn’t know them, it hurts me because they are Ukrainians. It also pains me to see children growing up without their parents because their parents are at the front. The war has intensified my sense of empathy and belonging.”
Her mental health has suffered. She says anxiety is ever-present in her life.
But what she returns to often as she answers questions about how her life is today compared to before the war is the loss she, and others, have experienced.
“What I miss most [from my life before the full-scale invasion] are the people who have been killed in the war. I have lost friends, acquaintances, and relatives. Nothing compares to human loss. The hardest thing I have had to deal with during this war is going to the funerals of friends — people you used to go to parties with, travel with, study with,” she says.
The human cost of Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine has been enormous – Ukraine’s government does not officially give figures for military casualties, but it has been estimated they could be up to 600,000 (Russian military casualties are thought to be more than twice that amount).
But the scale of civilian casualties has been huge, too. According to UN bodies, more than 15,000 civilians have been killed and over 41,000 injured in Ukraine since the start of the invasion on February 24, 2022.
Worryingly, as Ukraine marks the fourth anniversary of the start of the war, research suggests there has been a sharp increase in civilian casualties over the last year.
Data from Action on Armed Violence (AOAV), released earlier this month, showed civilian casualties in Ukraine increased by 26 percent in 2025 compared with 2024, despite there being a 6 percent drop in the number of injurious explosive weapon incidents recorded nationwide.
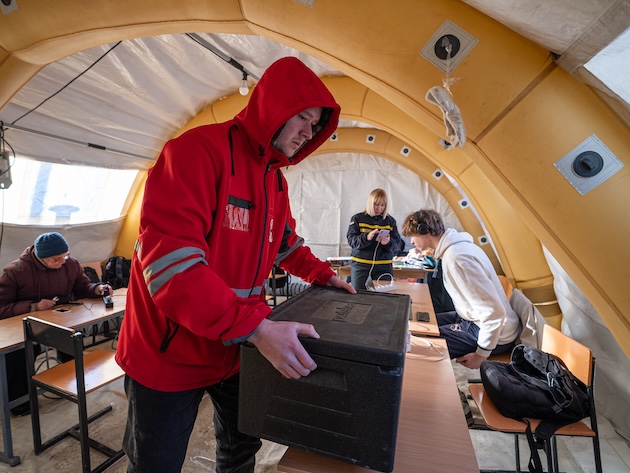

In Kyiv, response efforts continue amid attacks on energy infrastructure and severe cold. The Ukrainian Red Cross is supporting warming centres around the clock, providing people with a safe place to warm up, receive assistance, and feel cared for during difficult conditions. Credit: Red Cross
The group said its data showed a worrying shift in the character of the conflict – the average number of civilians killed or injured per incident in Ukraine rose 33 percent over the year, with a total of 2,248 civilians reported killed (an 11 percent rise) and 12,493 injured (a 28 percent rise) by explosive violence.
This suggests that explosive weapons are being used by Russia in Ukraine in ways that generate greater civilian impact, whether through more drone strikes, heavier munitions, specific targeting choices of populated areas, or repeated strikes on urban infrastructure, the group said.
Nearly seven in ten civilian casualties recorded in AOAV data occurred in residential neighbourhoods, up from just over four in ten in 2024.
Niamh Gillen, a researcher at AOAV, told IPS it was impossible to definitively say that Russian forces were deliberately targeting Ukrainian civilians, but that “the data speaks for itself.”
“It shows that civilian areas are being attacked, that the attacks are occurring within civilian areas like hospitals, schools, cities, towns. In general, in areas where civilians are heavily concentrated, like cities and towns, villages, anywhere like that, if you’re using an explosive weapon with wide area impacts, then you’re likely to harm more civilians,” she said.
On top of the deaths and destruction Russian attacks have caused, they have also led to massive displacement. It is thought that at least 3.4 million people are internally displaced in the country. This has put massive pressure not just on the displaced themselves, but also on host communities and services.
People’s physical health has deteriorated in such conditions – the World Health Organisation (WHO) has said that more than two-thirds of the population have reported a worsening of their health since the start of the invasion.
But the harm caused by these attacks is far from just physical. Mental health professionals in the country, as well as international bodies including the WHO, have warned of a mental health crisis in Ukraine, with possibly up to 10 million people suffering with mental health problems.
IPS spoke to scores of people in cities and towns across Ukraine about how the war had affected their mental health. Many spoke of experiencing anxiety, sometimes permanently to some level, which could be intensified at any moment by the frequent sound of air raid sirens warning of an attack, or for those closer to frontlines, the sounds of explosions and bombings.
“What affects my mental health on a daily basis are the constant nighttime drone and missile attacks. Because of them, it is impossible to relax or get proper rest, as reaching a shelter for safety is essential, even at night,” Mihail*, a teenager who lives in the Kyiv region, told IPS.
The situation for many Ukrainians has acutely worsened this winter. In what has been one of the coldest winters the country has seen for many years, Russian forces have repeatedly attacked Ukraine’s energy infrastructure, resulting in massive, widespread power outages. Thermal heating facilities have also been destroyed in targeted attacks.
As temperatures have plunged to as low as minus 30 degrees Celsius on some occasions, millions of people have been left freezing in their homes.
Jaime Wah, Deputy Head of Delegation with the International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (IFRC) in Ukraine, said people were suffering desperately in the cold.
“Some nights have been very unbearable. There is no escape from the cold. When you leave your apartment, it’s cold. Sometimes people have been joking that it’s warmer inside a fridge than inside their apartment. I’ve been here for over four years now, and it’s been the worst winter,” she told IPS.
Humanitarian organisations, including the Ukrainian Red Cross, and state emergency services have set up emergency heating points in cities and towns where people can keep warm, recharge devices and get food.
But Wah said while this has become a humanitarian crisis, it is one of just many crises Ukrainians are battling.
“In frontline regions, there are communities that are under evacuation orders, and some communities have essentially had most of their resources cut off. Family ties are quite strained – mental health needs are also immense, not only in the frontline regions but across Ukraine,” she said.
“There are lots of repairs to homes that are needed, not to mention the energy crisis, which is a humanitarian crisis… with no heating and no electricity, just the day-to-day things – just even heating your food becomes a problem. A lot of families are having to spend more time outside their homes, having to spend more money. On top of that, the cost of living has increased. These are some of the real, tangible situations that people in Ukraine are facing now,” she added.
Amid these problems, many Ukrainians admit that they are exhausted after four years of war.
But among the many people IPS spoke to on the eve of the fourth anniversary of the war, there was a widespread, although certainly not universal, determination to not give up.
“I feel a sense of responsibility. I do not have the right to give up, because many people have died so that I could have the chance to live. Of course, there is exhaustion, but, unlike those in the military, a civilian like me has time to rest and reset,” said Iryna.
For many, such resilience is born out of a desire not just for them and their country to survive what they see as Russia’s attempt to destroy them as an independent state and nation, but also a hope that, ultimately, there will be some justice served for what has been done to them.
The Russian military and authorities have repeatedly been accused of war crimes, crimes against humanity, breaches of international humanitarian law, as well as genocide, during the invasion of Ukraine.
The sheer volume of alleged crimes – at least 180,000 war crimes have been registered by Ukraine’s Prosecutor General – and the constraints of documenting, investigating and prosecuting during an ongoing conflict mean that bringing those behind them to justice was never expected to be easy. Only over 100 people have been prosecuted in Ukraine so far for crimes during the invasion.
But there are fears that international bodies such as the International Criminal Court (ICC), which has issued an arrest warrant for, among others, Russian President Vladimir Putin over alleged war crimes, could be rendered increasingly toothless in their ability to ever prosecute major figures who ordered such crimes because world leaders, such as US President Donald Trump, are no longer interested in upholding international justice for war crimes.
“I truly hope that the war will end very soon and that all war criminals will be brought to justice. However, what I see happening right now is the opposite: while institutions like the UN are unable to punish Russia, people are starting to forget about its war crimes. Countries are gradually lifting sanctions,” said Mihail.
“For example, Russian athletes are going to be able to take part in the Paralympics this year. As a result, people who committed war crimes just months or years ago can now take part in one of the world’s biggest sporting events. So we need to act – by refusing to normalise aggression, keeping sanctions firm and, most importantly, remembering about war.”
Others, though, are more hopeful.
“There is no doubt among Ukrainians that war criminals can be brought to justice,” Oleh Martynenko, an expert at the Ukrainian NGO Center for Civil Liberties, which documents war crimes, told IPS.
“This is evidenced by the participation of Ukrainians in international missions and courts where war criminals have been convicted. Also, thanks to the European Union, Ukrainians are building their own criminal prosecution systems, which provide for the arrest and imprisonment of Russian war criminals in accordance with UN international standards,” he said.
Regardless of these concerns and the other problems Ukrainians are facing as the full-scale invasion goes into its fifth year, some are looking to the future with a degree of hope.
“I feel a mix of determination, resilience, anger, and hope of victory,” Tetiana, a nurse in the Dnipropetrovsk region, who asked not to be identified for security reasons, told IPS. “Glory to Ukraine!” she added.
*Name changed to protect identity.
IPS UN Bureau Report