Active Citizens, Civil Society, Climate Action, Climate Change, Climate Change Justice, Conferences, COP30, Crime & Justice, Development & Aid, Economy & Trade, Energy, Environment, Freedom of Expression, Global, Headlines, Indigenous Rights, Latin America & the Caribbean, Press Freedom, TerraViva United Nations
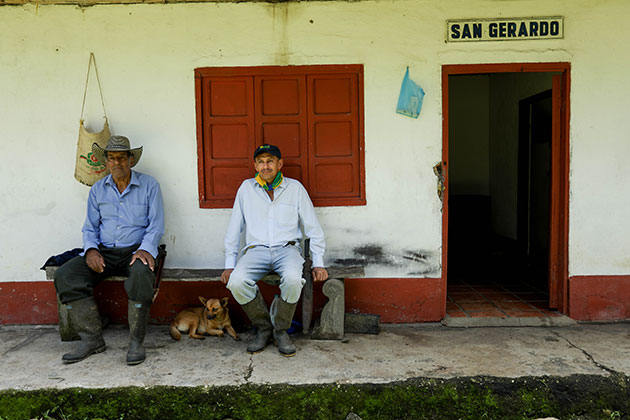

Family agriculture and land defenders in Colombia. Credit: Both Nomads/Forus
– As the world prepares for the next COP30 summit, a quieter battle is raging in courtrooms. Strategic Lawsuits Against Public Participation (SLAPPs) are the fossil-fuel industry’s new favourite weapon, turning justice systems into instruments of intimidation.
“Speak out, and you’ll pay for it”
On a humid morning in August 2025, two small environmental groups in Panama — Centro de Incidencia Ambiental and Adopta Bosque Panamá — found out through social media that they were being sued for “slander” and “crimes against the national economy.” Their offence? Criticising a port project on the country’s Pacific coast.
A few days later, across the border in Costa Rica, two environmental content creators woke up to find their bank accounts frozen and salaries withheld. Their “crime” was posting videos about a tourism project they said was damaging Playa Panamá’s fragile coastline.
In both cases, the message was straightforward: speak out, and you’ll pay for it.
These are part of a growing global trend that is particularly ominous as climate activists, Indigenous defenders, and journalists push their demands upon the upcoming COP30 negotiations. The battle to protect the planet increasingly comes with an additional cost: defending yourself in court.
SLAPPs: Lawsuits Designed to Scare, Not Win
The acronym sounds almost trivial — SLAPP — but its impact is anything but. SLAPP stands for Strategic Lawsuits Against Public Participation, a term coined decades ago to describe legal actions intended not to win on merit but to intimidate, exhaust, and silence those who speak out on matters of public interest.
According to Transparency International, “SLAPPs are also known as frivolous lawsuits or gag lawsuits, as they silence journalists, activists, whistleblowers, NGOs and anyone who brings facts to light in the public interest.”
These are not just lawsuits; they are in fact strategy. They don’t need to win, they just need to drain your time, your money, and your hope.
The claimants are usually powerful, ranging from corporations, politicians, or investors.
In the Costa Rican case, the company linked to the Playa Panama tourism project did not even allege material harm. Yet the court imposed “precautionary embargoes,” blocking credit cards, freezing wages, even restricting property rights, punishing through the process.
In Panama, the developers of the Puerto Barú port project filed a criminal complaint against environmental NGOs who had challenged the project’s environmental impact assessment before the Supreme Court. Those challenges are still pending. Rather than waiting for the judiciary’s ruling, the company launched a separate legal attack, accusing those NGOs of harming the national economy.
Observers call it “judicial intimidation.” The case triggered several alerts across the EU SEE Early Warning Mechanism, warning of a “chilling effect on civic participation.”
‘Unfortunately, in Panama, judicial harassment of journalists and activists by politicians and businesspeople is already common practice because criminal law allows it. Reform is needed in relation to so-called crimes against honour and the grounds for seizure of assets. International organisations such as the Inter-American Press Association have warned about this,’ says Olga de Obaldía, executive director of Transparency International – Panama Chapter, a national member of the EU SEE network.
In Costa Rica, the embargoes imposed on content creators Juan Bautista Alfaro and Javier Adelfang sparked outrage. Within days, 72 organisations and more than 3,000 individuals — from academics to Indigenous leaders — signed an open letter condemning the action as “an assault on public interest advocacy.”
The backlash worked: members of the Frente Amplio Party introduced a bill to restrict the use of preventive embargoes in cases involving public interest speech.
But for those already targeted, the damage – emotional, financial and reputational – has already been done.
We do not just see SLAPPs deployed in Latin America. Examples of SLAPPs as a means of lawfare by the rich and powerful have been around for a long time across the globe.
In Thailand, Thammakaset sued several members of the NGO Fortify Rights and other activists for denouncing abusive working conditions. Still today content posted by communities or NGOs, or even comments under local government posts, are often picked up and turned into criminal defamation cases.
Despite the existence of anti-SLAPP provisions in the Criminal Procedure Code, experiences indicate that they are largely ineffective. The constant threat of facing litigation based on online content disrupts CSO work and chills free speech.
Climate Activism Under Pressure
As the world heads toward another global climate summit in Brazil – where journalist Amanda Miranda faces a SLAPP by government officials for uncovering corruption – we face a paradox: while governments make promises about protecting the environment, environmental defenders are being prosecuted for holding them accountable.
Brazil’s baseline snapshot on an enabling environment also highlights a related trend: environmental defenders are frequently framed as “anti-development,” a narrative used to delegitimise their work and undermine public support. SLAPPs reinforce this strategy. Beyond draining time and resources, these lawsuits inflict reputational harm, serving as tools in broader campaigns to discredit and silence critics.
According to research from the Business & Human Rights Resource Centre, the highest number of SLAPPs – almost half of them – took place in Latin America, followed by Asia and the Pacific (25%), Europe & Central Asia (18%), Africa (8.5%), and North America (9%). Nearly three-quarters of cases were brought in countries in the Global South and 63% of cases involved criminal charges. Furthermore, most individuals and groups facing SLAPPs raised concerns about projects in four sectors: mining, agriculture and livestock, logging and lumber, and finally palm oil.
In an International Center for Non-Profit law – ICNL – study on over 80 cases of SLAPPs across the Global South, out of them “91% were brought by private companies or company officials(…) 41% brought by mining companies and (…) 34% brought by companies associated with agriculture.”
According to data from the CASE Coalition, SLAPP cases have risen sharply in recent years: from 570 cases in 2022 to over 820 in 2023 in Europe alone. Around half of those targeted climate, land, and labor rights defenders. Fossil fuel and extractive industries remain the most frequent initiators.
It is important to remember that those numbers under-represent the extent of SLAPP use, they are based on reported legal cases and can’t include the many cases in which the mere threat of a lawsuit was enough to silence before filing a complaint
The Business & Human Rights Resource Centre has documented that companies linked to mining, tourism, and large infrastructure projects are increasingly using SLAPPs to paralyse critics ahead of international events like COP, when scrutiny intensifies.
The danger of SLAPPs lies in their quietness. They happen behind closed doors, in legal language, far from the marches and hashtags. The trials often do not even end up in lawsuits. Yet their effect is profound. Every frozen bank account, every unpaid legal fee, every public apology extracted under duress weakens the collective courage needed to hold power to account.
Across regions, SLAPPs follow the same playbook: identify outspoken defenders, sue them on vague charges like “defamation” or “economic harm”, drag the process out for years, win by exhausting, not convincing.
Of course, the specific tactics vary by legal context. In some countries, certain charges carry strategic advantages. For example, in the Philippines, authorities frequently rely on serious, non-bailable allegations — including charges like illegal possession of firearms — to keep activists detained for extended periods.
The Philippines remains the most dangerous country in Asia for land and environmental defenders with frequent attacks linked to mining, agribusiness, and water projects.
Political repression persists and civil society groups continue to face “red-tagging” and SLAPPs, further enabled by the passage of the Anti-Terrorism Act, the Anti-Money Laundering Act of 2001, and the Terrorism Financing Prevention and Suppression Act of 2012.
Authorities have also used fabricated firearms and explosives charges to target activists, journalists, and community leaders, often accompanied by asset freezes, surveillance, and prolonged detention. In these settings, SLAPPs can “weaponise” the criminal justice system itself to remove critics from public life entirely.
SLAPPs have become the invisible front of the climate struggle, a slow-motion suppression campaign that rarely makes headlines.
Tactics to Fight Back
In early 2024, the European Union adopted its first-ever Anti-SLAPP Directive, a milestone achievement after years of campaigning by journalists and civil society. It sets out minimum standards to prevent abusive lawsuits and protect public participation.
But implementation remains uncertain. The Vice-President of the European Commission, Vera Jourova, called the Directive “Daphne’s law,” in memory of the Maltese journalist Daphne Caruana Galizia, who was killed in 2017 while she was the victim of numerous legal proceedings against her, and whose tragic story helped raise awareness of the issue.
Beyond the European context, similar efforts to counter SLAPPs have emerged elsewhere, for example in Colombia with the Guerra v. Ruiz-Navarro case. This case illustrates the importance of investigating sexual violence and abuse of power, recognising it as a matter of public interest that warrants protection. This ruling sets a strong precedent against the misuse of courts to silence the press by influential figures and underscores that defending victims and informing the public are acts of defending human rights.
In Indonesia, another country where SLAPPs are being deployed, civil society groups continue to advocate for stronger legal protections, including legislation to protect from SLAPPs. A small step forward came in September 2024, when the Ministry of Environment and Forestry issued Regulation No. 10/2024, on legal protection for environmental defenders.
“While the Ministry of Environment and Forestry Regulation No. 10/2024 represents an initial step toward safeguarding environmental defenders, civil society organisations expect its effective implementation, coupled with broader anti-SLAPP legislation, to ensure comprehensive protection against retaliatory lawsuits and foster a secure environment for public participation in environmental governance,” says Intan Kusumaning Tiyas of INFID, national civil society platform in Indonesia.
Civil society groups are calling for action on immediate priorities.
These include stronger legal safeguards by enacting robust national anti-SLAPP laws that allow for early case dismissal, ensure defendants can recover legal costs, and penalise those who file abusive lawsuits.
Setting up solidarity and support through regional and global networks can quickly mobilise legal assistance, mental health support, and emergency funding for those targeted.
Finally, actions around visibility and accountability are needed to bring SLAPPs into the public eye and raise awareness. SLAPPs need to be framed not as ordinary legal conflicts, but as violations of human rights that weaken an enabling environment for civil society, democratic participation and obstruct climate justice.
At COP30, negotiators will debate carbon credits and transition funds. But the real test of climate commitment may lie in whether states protect the people defending rivers, forests, and coastlines from powerful interests.
Civil society hopes to push a bold message into COP30 discussions: defending the environment requires defending those who defend it and supporting an enabling environment for civil society.
This article was written with the support of the Forus team, particularly Lena Muhs, and members of the EU SEE network.
IPS UN Bureau