Africa, Civil Society, Crime & Justice, Economy & Trade, Featured, Gender, Headlines, Human Rights, Labour, Press Freedom, TerraViva United Nations

Credit: Zohra Bensemra/Reuters via Gallo Images
– Civic space is deteriorating in Senegal ahead of next February’s presidential election. Recent protests have been met with lethal violence and internet and social media restrictions. Senegal’s democracy will soon face a key test, and whether it passes will depend largely on whether civic space is respected.
Political conflict
Recent protests have revolved around the populist opposition politician Ousmane Sonko. Sonko came third in the 2019 presidential election and has grown to be the biggest thorn in President Macky Sall’s side. He’s won support from many young people who see the political elite as corrupt, out of touch and unwilling to tackle major social and economic problems such as the country’s high youth unemployment. He’s also been the subject of a recent criminal conviction that his supporters insist is politically motivated.
On 1 June, Sonko was sentenced to two years in jail for ‘corrupting youth’. This resulted from his arrest on rape charges in March 2021. Although he was cleared of the most serious charges – something women’s rights advocates have expressed concern about – his conviction likely makes him ineligible to stand in the next presidential election.
Sonko’s arrest in March 2021 triggered protests in which 14 people died. His conviction set off a second wave of protests. Sonko was arrested again on 28 July on protest-related charges, including insurrection. A few days later, the government dissolved his party, Pastef. It’s the first such ban since Senegal achieved independence in 1960.
All of this gave fresh impetus to Sonko’s supporters, who accuse the government of instrumentalising the judiciary and criminal justice system to stop a credible political threat.
Repressive reaction
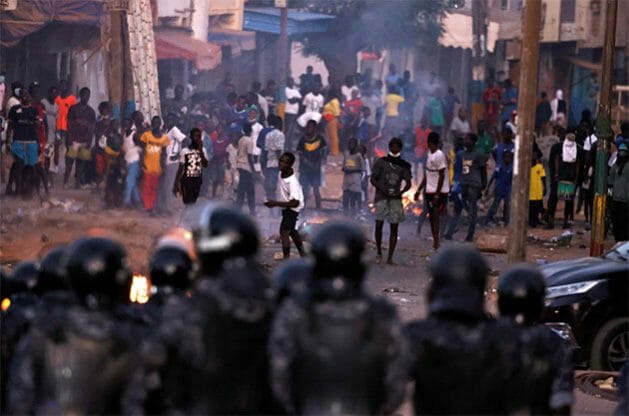
The latest wave of protests saw instances of violence, including stone-throwing, tyre burning and looting. The state responded with lethal force. According to civil society estimates, since March 2021 over 30 people have been killed, more than 600 injured and over 700 detained.
In response to the recent protests, the army was deployed in the capital, Dakar. Live ammunition was used and armed people dressed in civilian clothes, evidently embedded with security forces, violently attacked protesters.
Journalists were harassed and arrested while covering protests. Recent years have seen a rise in verbal and physical attacks on journalists, along with legal action to try to silence them. Several journalists were arrested in relation to their reporting on Sonko’s prosecution. Investigative journalist Pape Alé Niang has been jailed three times in less than one year.
The government also limited internet access and TV coverage. TV station Walf TV was suspended over its protest coverage. On 1 June, social media access was restricted and on 4 June mobile internet was shut down for several days. In August, TikTok access was blocked. Restrictions harmed both freedom of expression and livelihoods, since many small traders rely on mobile data for transactions.
⚠️ Confirmed: Metrics show the restriction of social media and messaging platforms including Twitter, Facebook, WhatsApp, Instagram and YouTube in #Senegal; the incident comes amid protests over the sentencing of opposition figure Ousmane Sonko
📰 Report: https://t.co/2ckQPxJ5j3 pic.twitter.com/MuohanLeCP
— NetBlocks (@netblocks) June 1, 2023
Third-term tussle
A major driver of protests and Sonko’s campaign was speculation that Sall might be tempted to seek a third presidential term. The constitution appeared to be clear on the two-term limit, but Sall’s supporters claimed constitutional amendments in 2016 had reset the count. Thousands mobilised in Dakar on 12 May, organised by a coalition of over 170 civil society groups and opposition parties, to demand that Sall respect the two-term limit.
On 3 July, Sall finally announced that he wasn’t running again. But it hasn’t ended suspicion that the ruling Alliance for the Republic (APR) party will go to any lengths stay in power, including using the state’s levers to weaken the opposition.
There’s precedent here: ahead of the Sall’s re-election in 2019, two prominent opposition politicians who might have presented a serious challenge were excluded. In both cases, barely weeks before the election the Constitutional Council ruled them ineligible due to prior convictions on corruption charges that were widely believed to have been politically motivated.
That Sonko and Pastef might have stood a chance in 2024 was suggested by the results of votes in 2022. In local elections, the APR lost control of Dakar and Sonko was elected mayor of Ziguinchor city. And then in parliamentary elections, the APR lost 43 of its 125 seats and Pastef finished second, claiming 56 seats, leaving no party with a majority.
Reputation on the line
Senegal long enjoyed an international reputation for being a relatively stable and democratic country in a region that’s experienced numerous democratic setbacks. With West African countries such as Burkina Faso, Guinea, Mali and now Niger under military control, and others like Togo holding deeply flawed elections, Senegal stood out. It’s held several free elections with changes of power.
The country’s active and youthful civil society and relatively free media have played a huge part in sustaining democracy. When President Abdoulaye Wade sought an unconstitutional third term in 2012, social movements mobilised. The Y’en a marre (‘I’m fed up’) movement got out the youth vote to oust Wade in favour of Sall. Wade himself rode a similar youth wave in 2000. So Sall and his party are surely aware of the power of social movements and the youth vote.
A small step forward was taken recently when parliament voted to allow the two opposition candidates who’d been blocked in 2019 to stand in 2024. But the government needs to do much more to show its commitment to democratic rules.
Upholding protest rights would be a good start. The repeated use of violence and detention of protesters points to a systemic problem. No one has been held to account for killings and other rights violations. It’s high time for accountability.
Media freedoms need to be respected and people detained for exercising their civic freedoms must be released. For Senegal to live up to its reputation, Sall should strive to enter history as the president who kept democracy alive – not the one who buried it.
Andrew Firmin is CIVICUS Editor-in-Chief, co-director and writer for CIVICUS Lens and co-author of the State of Civil Society Report.