Active Citizens, Africa, Civil Society, Crime & Justice, Democracy, Energy, Featured, Headlines, Human Rights, Labour, Press Freedom, TerraViva United Nations

Credit: Pascal.Van, licensed under CC BY-SA 2.0
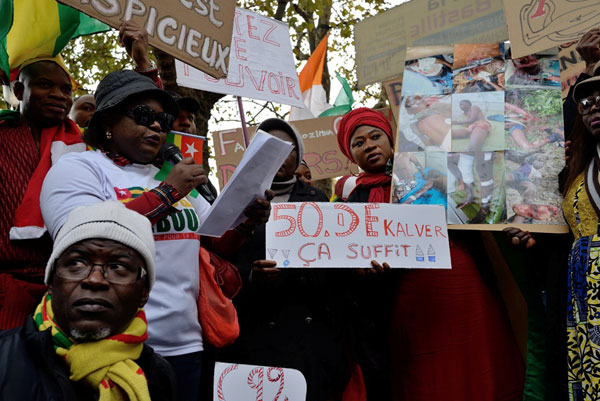
– In late June, thousands flooded the streets of Lomé, Togo’s capital, presenting the ruling dynasty with its biggest challenge in decades.
The catalyst was constitutional manoeuvring by President Faure Gnassingbé to maintain his grip on power. In March 2024, his government pushed through constitutional amendments that transformed Togo from a presidential to a parliamentary system. This created a new position, the President of the Council of Ministers – effectively Togo’s chief executive – elected by parliament rather than by popular vote, and with no term limits. Gnassingbé assumed this new role in May, making it abundantly clear the changes were only about keeping him in power indefinitely.
This constitutional manoeuvre was the latest episode in a 58-year family saga that began when Faure’s father, Gnassingbé Eyadéma, seized power in a 1967 coup. For 25 years, the elder Gnassingbé ruled over a one-party state, staging ritual elections that reached absurd heights in 1986 when he claimed re-election with close to 100 per cent of votes on an implausible 99 per cent turnout. Even after nominal multiparty democracy arrived in 1992, elections remained charades with predetermined outcomes, as opposition parties faced systematic obstacles that made fair competition impossible.
When Eyadéma died in 2005, the military simply appointed his son Faure as successor, despite the constitution mandating immediate elections. International pressure forced a hastily organised vote, but this followed the familiar script of violence, fraud and repression. The pattern repeated in 2010, 2015 and 2020, with each election offering a veneer of legitimacy for continued authoritarian rule – and eliciting successive waves of protest that were either violently repressed or pre-emptively suppressed.
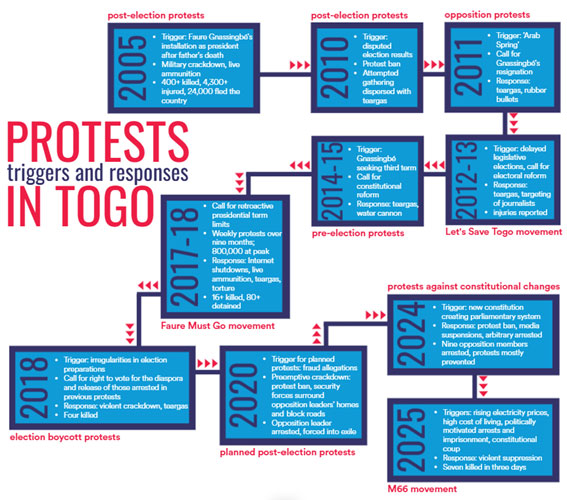
Now, two decades after Faure took power, this latest constitutional gambit has triggered the most significant challenge to his rule. The constitutional changes designed to keep him in power have instead galvanised opposition, creating a focal point for decades of accumulated grievances.
The current protests differ from their predecessors by being overwhelmingly led by young people who’ve never known any other leaders than the Gnassingbés. Raised on promises of multiparty democracy, they’ve witnessed systematic electoral fraud to perpetuate a government wholly unresponsive to their needs. They connect their daily struggles with unemployment, power outages and crumbling infrastructure with the long-term denial of their democratic freedoms.
The arrest in May of a popular rapper and TikToker, Aamron – for posting a video calling for street protests to coincide with Gnassingbé’s birthday on 6 June – galvanised discontent, turning simmering frustration into organised resistance. Aamron’s detention sparked the formation of the 6 June Movement (M66), led by young artists, bloggers, diaspora-based activists and civil society figures who rely heavily on social media to coordinate protests, bypassing state-controlled channels.
The government’s response, however, has followed a familiar path of authoritarian crackdown. In late June, security forces killed at least seven people, including 15-year-old Jacques Koami Koutoglo, and they’ve also used teargas, beatings and mass arrests against protesters. The regime has detained journalists, forced deletion of protest footage and imposed internet shutdowns during protests. It has suspended international media outlets including France 24 and RFI for their protest coverage. it has even issued international arrest warrants for M66 leaders based abroad, accusing them of terrorism and subversion.
Protests have continued despite repression. The leadership of young people, less intimidated by the security apparatus and better connected through social media, has allowed for the diversification of opposition tactics, with activists shifting between street protests, legal challenges and international advocacy as circumstances dictate. The diaspora is also playing a role, with Togolese communities abroad organising solidarity protests and advocating with international organisations for sanctions against the Gnassingbé regime.
Significant obstacles however remain. Gnassingbé controls all levers of power, including security forces, the electoral commission and the Constitutional Court. For a democratic transition to result, international pressure would need to intensify, including the imposition of targeted sanctions on regime officials and their economic interests. Regional bodies, particularly the Economic Community of West African States, would need to act, including by threatening to suspend Togo until democratic reforms are implemented.
Whether these protests trigger democratic change or become yet another chapter in the history of repressed dissent will ultimately depend on the ability of pro-democracy forces to sustain pressure and whether the international community finally decides to act. Gnassingbé’s constitutional manoeuvre may prove to be his final act, not because it succeeded in keeping him in power, but because it awakened a new generation. Togo’s young people have discovered the power of collective action—and that could prove decisive.
Inés M. Pousadela is CIVICUS Senior Research Specialist, co-director and writer for CIVICUS Lens and co-author of the State of Civil Society Report.
For interviews or more information, please contact research@civicus.org












