Civil Society, Crime & Justice, Economy & Trade, Education, Gender, Gender Violence, Global, Headlines, Health, Human Rights, Humanitarian Emergencies, Inequity, Labour, Poverty & SDGs, TerraViva United Nations
The following opinion piece is part of series to mark the upcoming International Women’s Day, March 8.
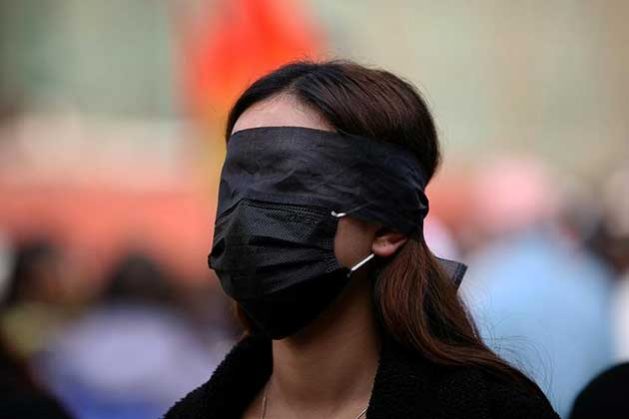

Protest for women’s rights in Kathmandu, Nepal. Credit: Sanjog Manandhar
– Today, despite centuries of activism and mobilisations, women and non-binary people continue to remain disadvantaged in almost every sphere – from “public life” to the “shadow pandemic” of gender-based violence.
In light of COVID-19, some struggles have been considered in theory, but most continue to be ignored in practice. How can we dismantle the “gender lies” perpetuating in the 21st century? How do we start taking into account the diverse experiences of women, without excluding black and indigenous voices on the basis of power and privilege?
Afghanistan, Nepal, Bolivia, Mexico and Uganda: five activists tell us how they transform the ways their communities think and act around gender.
Afghanistan: rap music to save child brides
Sonita Alizadeh, is a survivor of two attempts at forced marriage, and now a rapper and activist fighting for the liberation of women against forced marriage. Born in Herat, Afghanistan, under the Taliban regime, she grew up in Iran, as a refugee with her family. At 10 years old, she narrowly escaped a forced marriage. Her family again tried to sell her when she was sixteen, she escaped. Afghanistan has the 20th highest number of women married before the age of 18 in the world, with 28% of Afghan girls married off as minors, according to Girls Not Brides.
“My mother was a child bride, and she did not meet her husband until their wedding day. By marrying me off at a young age, she was simply repeating the cycle. This tradition makes me want to raise awareness of this harmful issue with the help of millions of others around the world through my music,” says Sonita in an interview with Forus.
Witnessing her friends swiftly disappearing as they were forced to marry, Sonita wrote the song “Daughters for Sale”, which kick-started her work as a human rights activists and rapper.
“Music touches people in a way words cannot – it is deeper and more emotional. People listen to music and young people pay attention to the lyrics. Music can be a powerful way to hear important messages. That is why I always rap about things that need to change in the world, or ideas that young people need to hear, to dream big.”
Today, Sonita uses her tracks and success to give young girls self-confidence. She sings to tell: “Hold this hope in your heads and your hearts. Hold this hope for the future. Never give up.”
Nepal: Fighting “period poverty”.
As 2020 drew to a close, protesters across South Asia took to the streets and to social media, calling on their governments to end the perpetuating cycle of widespread sexual violence against women and children.
In Nepal, hundreds of activists returned to the streets after a 17-year-old girl was raped and strangled to death. Some protesters wore black over their eyes to symbolize public authorities closing their eyes to sexual violence. Activists say that although the country’s constitution guarantees equal rights to women, there is a clear disjunction between theory and practice.
“How do we make sure that there is no gap between law and social progress?” asks Jesselina Rana, a human rights lawyer, co-founder with engineer Shubhangi Rana of Pad2Go, a social enterprise focusing on menstrual health and the taboos surrounding it.
It is estimated that around 83 percent of menstruating individuals face some form of restriction or exclusion during their menstrual cycle in Nepal.
“From a very young age, menstruating individuals are made to believe that their menstrual cycle makes them impure, and it can only be talked about behind closed doors,” Jesselina explains.
With Pad2Go, Jesselina distributed over 80 sanitary napkin vending machines across Nepal. She collaborates with pad manufacturers, to provide pads at less than market rate in order to ensure affordability. She also organises discussions with both men and women to normalise conversations around menstruations.
“Nepal being a patriarchal society, men engagement is crucial to overcome social issues faced by women. Socially we need to get men into those spaces of conversation, at a young age, to make sure that everyone is part of the discussion to end the toxic cycle of gender discrimination.”
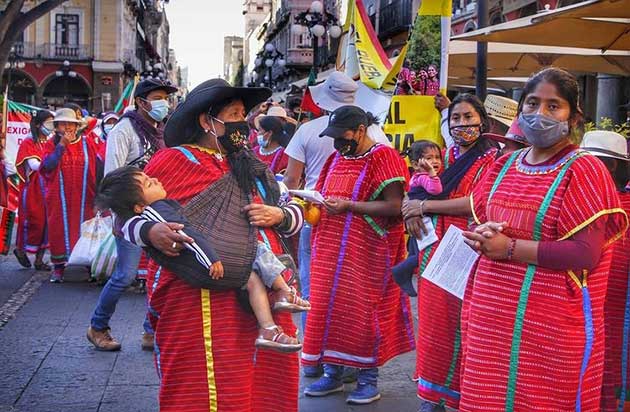

Protest in Mexico. Credit: Melanie Isahmar Torres Melo
Bolivia, Mexico: “Ni Una Menos”
Cradled in the “machismo culture”, Bolivia has one of the highest domestic violence rates against women in South America. The annual average of 110 femicides in the past 7 years persists, despite a 2013 law establishing measures to prevent and prosecute gender-based violence.
During the Covid-19 crisis, the economic consequences of the pandemic disproportionately affected Bolivian women. Government restrictions reduced access to food, aid programs did not adequately address the needs of communities, increasing their vulnerability and insecurity.
During the lockdown the slogan “Stay at Home” was widely promoted across Bolivia, yet for many women and girls victims of violence, that actually meant a very dangerous “Cállate en casa” (shut up at home), explains Iris Baptista from Red Unitas, a platform funded in 1976 that reunites 22 NGOs in Bolivia.
“Red Unitas created the campaign “SIN VIOLENCIA ES MEJOR” (Better Without Violence), to raise awareness of the fact that women are doing most of the work during the pandemic, to fulfil their role as mothers, wives and workers, yet they continue to face violence at home,” Iris explains.
But, violence against women and femicides are not just common in Bolivia—they are prevalent throughout the region. Global data is difficult to gather due to differences in reporting standards, however, the 2016 report, “A Gendered Analysis of Violent Deaths” founds that fourteen of the twenty-five countries with the highest femicide rates are Latin American.
Defined as “a pandemic within the pandemic”, gender-based violence has spiked since COVID-19 broke out. Writer Lynn Marie Stephen believes that laws and initiatives to protect women, “fail to indict the broader systems that perpetuate these problems, like social, racial, and economic inequalities, family relationships and social mores”.
“It’s not that there was less violence against women in the past, it’s just that it wasn’t made as visible as it is today,” says Melanie Isahmar Torres Melo, a photojournalist covering women issues in Puebla, Mexico.
Every day, 10 women are killed in Mexico. The number of femicides has increased by 137% in the past five years and reached its highest monthly rates in 2020. Despite this number, only 5% of all crimes committed in Mexico are punished. This dichotomy between numbers is often the result of a “single crime” vision, rather than a sociological phenomenon, linked to the idea of patriarchy and sexism.
“Most perpetuators are never caught; this has triggered ‘social anger’ around the issue of feminicides in Mexico. There is no respect for victims, they are blamed for being killed. New movements are rising led by different collectives and civil society organisations. People are taking to the streets and shouting “Ni Una Menos” no woman should be killed,” says Mela.
Uganda – creating an enabling environment for civil society
“I was arrested and shamed for leaked nudes”, model and activist Judith Heard explains. When nude pictures of her were published without her consent in 2018, she was widely criticized and was arrested under the Anti-Pornography Act. Her situation is far from unique, a survey conducted in 2016 found that 50% of Ugandan women aged between 15 and 49 has experienced violence by an intimate partner. As a result, in February 2019, Heard launched Day One Global, an advocacy organisation that seeks to curb sexual harassment and rape.
From Marion Kirabo who led a women’s protest against rising tuition fees, to Rosebell Kagumire, editor of the African Feminism digital platform opening “discussion and dialogue on feminist issues throughout the continent”, activists and “gender advocates” in Uganda, are creating innovative forms of “transnational feminism” both online and offline.
Yet, a recent report by Forus International, shows that only 1% of gender equality funding is going to women’s organizations worldwide, and that promoters of gender equality need increased protection. Even more worryingly, attacks on women organisations and civil society more generally, have been reinforced by the current COVID-19 crisis.
Overall, organizations that engage in monitoring the state’s conduct and advocate for human rights, anti-corruption, accountability, and democratic governance are experiencing growing obstacles. One of the most recent examples is the Uganda Communications Commission Guidelines for everyone posting content online, including bloggers and online news platforms, which aims to control people’s freedom of speech.
“While the Ugandan government welcomes the social services many civil society organizations provide, at the same time it feels threatened by the possibility of political mobilization and empowerment of the population that come with self-organized practices; needless to say, such threats to the government’s grip on power yield conflicts between the state and civil society actors,” according to the Uganda National NGO Forum, an umbrella organization with more than 650 member NGOs across the country.
#MarchWithUs
Despite the considerable progress, more than half of the world’s girls and women—as many as 2.1 billion people—live in countries that are not on track to reach key gender equality-related targets by 2030.
However, a new survey from Focus 2030 and Women Deliver, covering 17 countries on six continents—reveals that citizens are eager for sustained and strengthened political and financial investments to accelerate progress towards gender equality. In particular, the global public supports the need for women to play a role in all aspects of the COVID-19 pandemic response, with 82% of survey respondents on average saying they believe women should be involved in the response at all levels.
To build a recovery plan and a roadmap for the future, a gender lens must be applied. With the digital campaign #MarchWithUs, Forus is taking a full month to reflect on the voices of women and non-binary activists who are on the frontline of social change. It is time to act to turn “gender lies” into gender promises.
The authors are members of Forus Communication team.