Active Citizens, Civil Society, Crime & Justice, Economy & Trade, Featured, Headlines, Health, Human Rights, Labour, Middle East & North Africa, Migration & Refugees, Press Freedom, TerraViva United Nations

Credit: Georgios Kostomitsopoulos/NurPhoto via Getty Images
– The Islamic Republic of Iran has put down another uprising, with a ferocity that makes previous crackdowns seem restrained. The theocratic regime has survived, but it has done so by substituting violence for the economic security it cannot provide and the political legitimacy it no longer has. Its show of force is also an admission of weakness.
The protests that began on 28 December were triggered by a specific event — the collapse of the rial to a record low — but rooted in years of accumulated grievances. The second half of 2025 alone saw at least 471 labour protests across 69 Iranian cities. Inflation stood at 49.4 per cent. The 12-day war with Israel in June sent the Tehran Stock Exchange down around 40 per cent and cost many people their jobs. The United Nations Security Council reimposed sanctions in September. The government cut fuel subsidies in November and slashed exchange-rate subsidies in December. Over 40 per cent of Iranian households now live below the poverty line and around half the population consume fewer than the recommended 2,100 calories per day.
It was this collapse that brought typically conservative bazaar merchants onto the streets. Within two weeks, the protests had spread to all of Iran’s 31 provinces, drawing in the urban middle class, working-class communities and people from rural provinces who had historically been among the regime’s most reliable supporters. What began as an economic stoppage rapidly became political defiance. For the millions who joined the striking merchants, the plummeting currency and rising cost of food were not market failures; they were proof of the regime’s corruption and ineptitude. Generation Z played a central role, demanding not reform but profound change. Lethal repression provided further confirmation the system was beyond reform.
The state’s response evolved. Initially it offered token economic concessions alongside its usual crowd control violence such as batons and teargas. When it became clear that a widespread movement with political demands had taken hold, it shifted to total attrition. On 8 January, authorities imposed a near-total internet shutdown and authorised security forces to use military-grade weapons against crowds. The Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) – a parallel military structure, major political force and economic empire with a direct stake in the regime’s survival – spearheaded the crackdown, with its affiliated Basij paramilitary networks playing a central role in street-level violence.
The casualty figures were deliberately obscured by the internet blackout, but all evidence points in the same direction. Hengaw Organisation for Human Rights reported that at least 3,000 civilians — including 44 children — were killed in the first 17 days. Iran Human Rights, citing Ministry of Health sources, documented a minimum of 3,379 deaths across 15 provinces. The US-based Human Rights Activists News Agency reported around 7,000 verified fatalities by mid-February, with 12,000 further cases under review. Time magazine cited hospital records suggesting the toll may have reached 30,000. Even the lowest of these figures vastly eclipses the 537 deaths recorded during the 2022-2023 Woman, Life, Freedom protests. Supreme Leader Ali Khamenei’s concession that ‘several thousand’ had been killed confirmed the order of magnitude.
By 16 January the streets had been cleared, but a quieter repressive campaign continued, with nighttime raids, enforced disappearances and mass detentions in unofficial holding sites outside the legal system, targeting not only protesters but also doctors who treated the wounded, lawyers who provided legal assistance, bystanders who helped and people who posted supportive statements online. Authorities have detained over 50,000 people. Revolutionary Courts have fast-tracked mass indictments through summary trials, often conducted online and lasting mere minutes, with defendants denied independent legal counsel and confessions extracted under torture. Eighteen-year-old Saleh Mohammadi, whose retracted confession was obtained after interrogators broke bones in his hand, has been sentenced to be publicly hanged at the site of his alleged crime. Dozens more face imminent execution.
The regime has, for now, held: its security forces have not fractured, there have been no significant elite defections, and the IRGC has maintained its capacity for suppression. But it rules over a country with a wrecked economy, a battered nuclear programme, weakened regional proxies and a population that has run out of reasons to comply. Each protest cycle has required a higher threshold of state violence to suppress, a sign the regime has no other tool left.
What prevents weakness from becoming collapse is the absence of any alternative. The international response briefly suggested external pressure might tell – but did not. Donald Trump told Iranian protesters that ‘help is on its way’. The European Union listed the IRGC as a terrorist organisation. The UK imposed fresh sanctions. The Iranian diaspora held at least 168 protests across 30 countries. But the international noise simply enabled the regime to spread the narrative that the uprising was foreign-directed.
The exiled opposition is fragmented along ethnic, ideological and generational lines, seemingly more consumed by internal rivalries than the task of converting widespread discontent into sustained political pressure. Inside Iran, the most credible opposition voices — Nobel laureate Narges Mohammadi, reformist politician Mostafa Tajzadeh and veteran leader Mir Hossein Mousavi — are imprisoned or cut off from public life.
A weakened regime facing a leaderless opposition can endure, but what it cannot do is reverse its decay. Violence may clear the streets, but it cannot rebuild the economy, restore trust or give Iran’s young people a reason to stay. The regime has bought time, at an ever-rising price, but the crisis it’s suppressed isn’t going away.
Inés M. Pousadela is CIVICUS Head of Research and Analysis, co-director and writer for CIVICUS Lens and co-author of the State of Civil Society Report. She is also a Professor of Comparative Politics at Universidad ORT Uruguay.
For interviews or more information, please contact research@civicus.org


 Myanmar’s garment sector, which employs hundreds of thousands of workers, is in deep crisis. Since the coup, labour protections have collapsed, independent unions have been dismantled and workers who try to organise face intimidation, dismissal and arrest. Inside factories, reports show multiple cases of child labour, forced overtime, harassment, poverty wages and unsafe conditions. At the same time, rising living costs and US tariffs are pushing many workers further into insecurity as factories close and layoffs become more common. Garment workers, most of them women, are trapped between exploitation, repression and a rapidly shrinking industry.
Myanmar’s garment sector, which employs hundreds of thousands of workers, is in deep crisis. Since the coup, labour protections have collapsed, independent unions have been dismantled and workers who try to organise face intimidation, dismissal and arrest. Inside factories, reports show multiple cases of child labour, forced overtime, harassment, poverty wages and unsafe conditions. At the same time, rising living costs and US tariffs are pushing many workers further into insecurity as factories close and layoffs become more common. Garment workers, most of them women, are trapped between exploitation, repression and a rapidly shrinking industry.






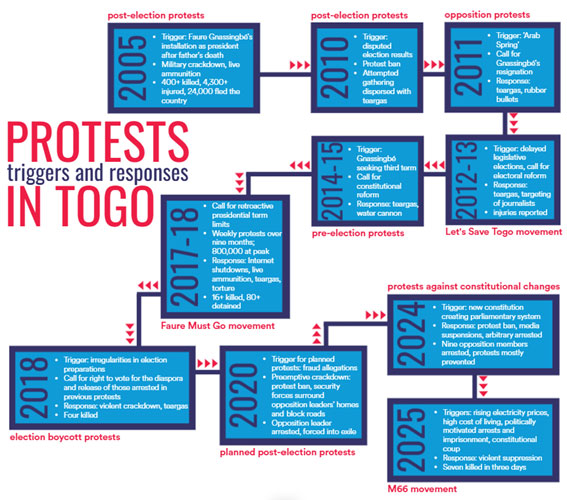
 The Angolan government’s 1 July decision to remove diesel subsidies, sharply pushing up public transport costs, triggered a series of
The Angolan government’s 1 July decision to remove diesel subsidies, sharply pushing up public transport costs, triggered a series of