1
(ThyBlackMan.com) The rapid rise of the Swahili language to global reach and importance, reflected in the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) designating 7 July 2022 as World Swahili Language Day, brings with it a deep sense of elation and satisfaction in the good work done to all those in Africa, the US and the world who worked hard to achieve this rightful recognition.
Certainly, Swahili has achieved the global presence and importance that demands international recognition and engagement for its contributions to communications, education, culture, economics, politics and diplomacy. It is the most widespread language in Africa, spoken in 12 countries (Tanzania, Kenya, Uganda, Democratic Republic of Congo, Rwanda, Burundi, Somalia, South Sudan, Mozambique, Malawi, Zambia, Comoros) and introduced into the educational systems of various other African countries viz. South Africa, Botswana and Namibia.
It is also spoken in Yemen and Oman and is considered one of the 10 most spoken languages ??in the world with over 200 million speakers. Both my organization, the African American Cultural Center (Us), and I are greatly honored, proud, and pleased to be a significant part of the worldwide effort that achieved this historic recognition and moment by studying, teaching, protecting, and spreading Swahili throughout the United States and protecting it. at national and international conferences and various other venues, formally and informally since 1960.
We have also inspired many African-American scholars and activists to adopt, study, teach, and share it in various ways. It has thus become the most widely used continental African language in the US in speaking, naming and practicing and promoting projects and programs organized around Kwanzaa and on Nguzo Saba.
My interest and perception of Swahili begins in the context, consciousness and practice of liberation. In Tanzania, President Mwalimu Julius Nyerere established Swahili as the unifying national language. And he gave refuge and support to freedom fighters from other African countries and they learned Swahili and Swahili in the process became the language of liberation.
It was the same for us in the US, especially in the Kawaida movement among organizations like the Us Organization, Uhuru Sasa, The East, The Institute of Positive Education, Ahidiana and others. And we spoke it and taught it in our homes, organizations, and independent schools, and used it in formulating Kawaida concepts of culture, community, liberation, and struggle.
Self-aware as African and seeking a cultural basis for how best to understand and assert myself in liberating, liberating, and life-enhancing ways, I turned to the study of Africa. I was a student at Los Angeles City College when I began to immerse myself in the independent study of Africa, its peoples, history and cultures, its leaders and liberation movements and social thought.
Here the Swahili word used by Mwalimu Nyerere to urge deep commitment, zhitumbukiza, is most appropriate. Because it speaks of a self-aware and dedicated person who throws himself deep into thought and practice to achieve a goal.
As a student and activist intellectual, deeply involved in the Black Liberation Movement, as an African and as part of entering African consciousness, I decided that I needed to know a continental African language. For me, it was a means of reclaiming a lost heritage, not just of language, but of a distinctly African way of knowing, thinking, relating, and being in the world that was embedded in language and reflected in the views, values, and practices that language yielded.
For me, it was a communal way of understanding and affirming ourselves in the world, a relational way that teaches interconnectedness, mutual respect, reciprocity and shared good in our lives and the world.
Here I chose Kiswahili and was immediately asked about this choice instead of other African languages. My choice of Swahili over another African language as our main heritage language was primarily because I saw it as Pan-African, the most common African language spoken in several African countries. And I reasoned that we African-Americans are a pan-African people, a new nation or national community, originating from and composed of the many ethnicities, peoples, and nations of Africa.
Second, as a pan-African language, Swahili is not tied to one ethnic group like other African languages ??and thus did not involve for me the choice of one ethnic language over another, but the choice of the most inclusive and inclusive African language, again pan-African in character and meaning to us.
Moreover, choosing Swahili was for me, for us, an act of freedom, of self-determination, a practice of resistance. It was part of our choice to be African, despite the dominant society’s schizophrenic practice of on the one hand calling us African to humiliate us, and then denying that we were African when we defiantly claimed or reclaimed our identity as an African people.
It is therefore no accident, but due to a crucial and defining historical moment, that our conversion to Africa and Swahili began at the height of the Black Freedom Movement, the African Independence Movements and similar liberation movements around the world. As Haji Malcolm taught, we “were living in an age of revolution, and the (African-American) rebellion was part of the rebellion against oppression and colonialism that characterized that age.”
And Swahili became the main basis for building, pursuing and interpreting this resistance against various forms of oppression, ie. racism, colonialism and imperialism.
At LACC, I had studied Arabic and continued to study French, but there were no Swahili classes. So I studied on my own until I transferred to UCLA, where I took classes and furthered my studies, benefiting greatly from exchanges with Swahili-speaking students, especially from Tanzania and Kenya. Once grounded in the language, I began to teach it not only as a skill but also as a cultural experience, an African way of understanding and engaging others in the world. This includes the teaching of culture, proverbial wisdom, Abunuwas stories and related cultural and philosophical concepts from across the global African community.
Having chosen Swahili as my preferred heritage language, I taught it in public institutions and on television in 1963 and 1964 respectively and privileged it in my varied lectures on history, community, culture and struggle. Also, in 1964 I introduced and taught Swahili classes at the Fremont Senior School in Los Angeles. The class was scheduled for two evenings a week, but was overbooked with 100 students and had to be rescheduled for two hours and four evenings.
The principal reported that one-third of the students were undergraduates, one-third college graduates, and the other third were ordinary people interested in learning an African language to regain a sense of heritage. Some were interested in visiting East Africa, others in preparing for foreign service as the Peace Corp, and still others were interested in learning the language as a way to connect meaningfully with their African heritage and learn the worldview and values ??embedded in and expressed by the language.
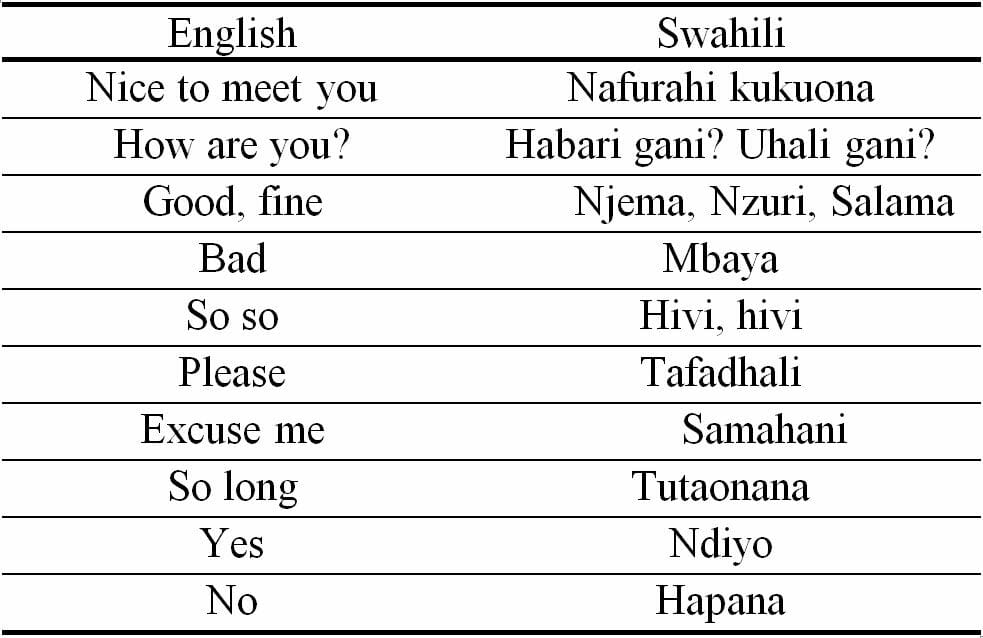
I have always emphasized the communal nature of language and culture. Thus, I would contrast the English words “See you later” with the words “Tutaonana” meaning “see you (later)” in Swahili, which emphasizes the collective and reciprocal nature of the Swahili statement. Or I would create a discussion around why we would use “kwetu“our place, the home of “kwango”, my place, even if you live alone, again emphasizing the relational nature.
Again, this emphasizes the relational nature of this African language and culture and the fundamental concept of man as a person in community, rich in relationships and corresponding responsibilities to bring and maintain good in the world.
Written by Dr. Maulana Karenga
Official website; https://www.maulanakarenga.org/
<!–
–> Source


















