Biodiversity, Climate Change, Conferences, Editors’ Choice, Environment, Europe, Featured, Global, Green Economy, Headlines, Natural Resources, Sustainable Development Goals, TerraViva United Nations
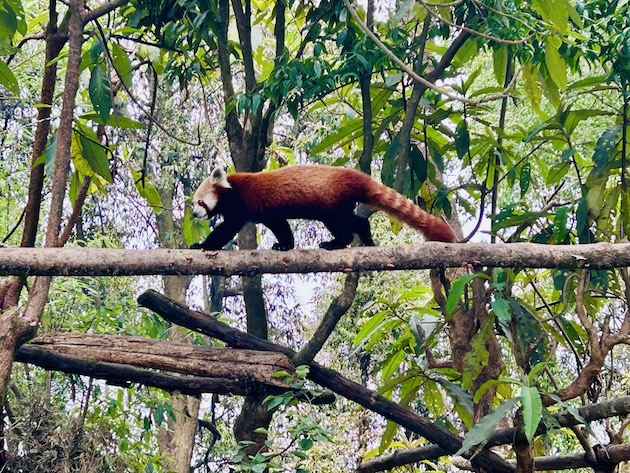

A red panda – labelled ‘endangered’ by the IUCN – at an animal sanctuary in the Indian state of West Bengal. As biodiversity loss accelerates, UNCBD is asking countries to take greater action to protect it. Credit: Stella Paul/IPS
– Governments meeting in Rome last week acknowledged that global efforts to protect nature are still not moving fast enough, even as biodiversity loss continues to affect ecosystems, livelihoods, and economies worldwide.
The warning came as the sixth meeting of the Subsidiary Body on Implementation (SBI-6) under the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) concluded after four days of negotiations focused on how countries are putting global biodiversity commitments into practice.
Held at the headquarters of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), the meeting is the first major checkpoint in a year of intensive talks leading to the United Nations Biodiversity Conference (COP17) in October in Yerevan, Armenia. There, governments will carry out the first global review of progress under the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework.
From Promises to Practice
At the centre of discussions in Rome was the challenge of turning global promises into action on the ground. The Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF), adopted in 2022, sets out 23 targets to be achieved by 2030, including protecting and restoring ecosystems, reducing pollution, cutting harmful subsidies, and ensuring fair sharing of benefits from genetic resources.
While most governments have formally endorsed the framework, SBI-6 revealed that implementation remains uneven. Negotiators worked through recommendations on biodiversity finance, national planning, gender equality, capacity-building, international cooperation, and access and benefit-sharing. Many of these were adopted without brackets, suggesting broad agreement.
“This has been a long week for all,” said Clarissa Souza Della Nina, Chair of the meeting, as she closed the afternoon plenary and announced that delegates would meet again in the evening. She noted that turning global ambitions into real action on the ground requires strong systems and institutions, and that this is not an easy process.
“The conclusion of SBI-6 marks an important early milestone in a very demanding year,” said Souza Della Nina, highlighting the efforts made by countries to work together and find common ground.
But behind the consensus language, discussions repeatedly returned to the same concern: global ambition is not yet being matched by national action.

SBI 6 Chair Clarissa Souza Della Nina, Brazil; Asad Naqvi, SBI 6 Secretary; and CBD Executive Secretary Astrid Schomaker celebrate the first conference room paper being approved. Credit: IISD/ENB, Mike Muzurakis
National Plans Show Mixed Progress
A key input to the Rome meeting was an analysis by the CBD Secretariat of national biodiversity strategies and targets submitted so far. These national plans are the main way countries translate the global framework into domestic policies.
The analysis covered 51 National Biodiversity Strategies and Action Plans (NBSAPs) and 130 sets of national targets. It found that while progress is being made, many plans fall short of the scale of change required.
About 75 percent of Parties have submitted national targets, but fewer have updated their full national strategies. Even among submitted plans, several global targets are only partially addressed. Social and economic aspects of biodiversity loss — including links to livelihoods, equity, and development — tend to receive less attention than conservation measures.
“These findings show clearly where we stand,” said Astrid Schomaker, Executive Secretary of the CBD. “They also show that countries still have the opportunity to raise ambition and speed up action before the global review.”
The first global review of progress under the KMGBF will take place at COP17. A major source of information for that review will be the seventh National Reports, which countries are required to submit by 28 February 2026.
By the end of SBI-6, the European Union, Lesotho, Uganda, and Switzerland had submitted their reports. Several other countries said they were close to completion, while others cited difficulties related to limited staff, technical challenges, or delays in accessing funds.
Delegates stressed that timely reporting is essential, not only for transparency but also to ensure that the global review reflects the realities faced by countries at different levels of development.
Gender and Inclusion Lag Behind
Another issue that drew attention in Rome was the limited integration of gender equality into biodiversity action. Under the global framework, countries have committed to ensuring the full and meaningful participation of women and girls, including those from indigenous peoples and local communities.
Yet the Secretariat’s analysis showed that only around 40 percent of national targets refer to gender-related issues, and only about 20 percent address women’s rights to land and natural resources. Even fewer countries reported involving women’s organisations in the preparation of national biodiversity plans.
For many participants, this gap was a reminder that biodiversity loss is not only an environmental issue but also a social one.
“Without addressing inequality, we will not succeed in protecting nature,” said Gillian Guthrie, a delegate from Jamaica, during the discussions, urging governments still updating their plans to take a more inclusive approach.
Money and Capacity Remain Major Hurdles
Financing biodiversity action was another recurring theme. Although the most detailed negotiations on biodiversity finance are scheduled for later this year, talks in Rome were informed by new studies on funding needs, the relationship between debt and biodiversity spending, and opportunities to better align biodiversity and climate finance.
Developing countries repeatedly pointed to limited financial resources, lack of access to technology, and institutional constraints as barriers to implementation. These challenges were reflected in the meeting itself, where several delegations consisted of a single representative struggling to follow multiple negotiating tracks.
The CBD Secretariat thanked donor countries that contributed to a special trust fund to support participation and called on others to do the same. Without broader support, delegates warned, global biodiversity decision-making risks leaving some voices unheard.
A decisive year ahead
The recommendations adopted at SBI-6 will now be forwarded to COP17, where governments will assess whether collective action so far is enough to meet the biodiversity targets set for 2030.
For many participants, the Rome meeting served as both a progress report and a warning. While cooperation is improving and more countries are engaging with the global framework, biodiversity loss continues to affect food systems, health, and economic stability, particularly in the Global South.
As delegates left Rome, the message was clear: the coming months will be critical. Whether the world can move from commitments to meaningful action will be tested in Yerevan, Armenia — and the stakes, many warned, could not be higher.
Below are some of the highlights of the 4-day meeting:
- The sixth meeting of the Subsidiary Body (SBI-6) on Implementation under the Convention on Biological Diversity began the first global review of how countries are acting to protect nature.
- An official analysis of national biodiversity plans showed progress but also revealed wide gaps between global goals and what many countries have committed to do at home.
- Around three-quarters of countries have submitted national biodiversity targets, but far fewer have updated full national strategies or addressed social and economic aspects of biodiversity loss.
- Gender equality and the participation of women, Indigenous Peoples, and local communities remain weak in many national plans, despite being central to the global biodiversity agreement.
- Developing countries highlighted ongoing challenges linked to limited funding, lack of technical capacity, and difficulty accessing resources needed to implement biodiversity actions.
- The outcomes from Rome will shape how global progress on biodiversity is measured and reviewed, setting the tone for accountability and action in the run-up to 2030.
IPS UN Bureau Report