Active Citizens, Armed Conflicts, Civil Society, Crime & Justice, Editors’ Choice, Featured, Global Governance, Headlines, Human Rights, IPS UN: Inside the Glasshouse, Middle East & North Africa, North America, Peace, Press Freedom, Regional Categories, TerraViva United Nations
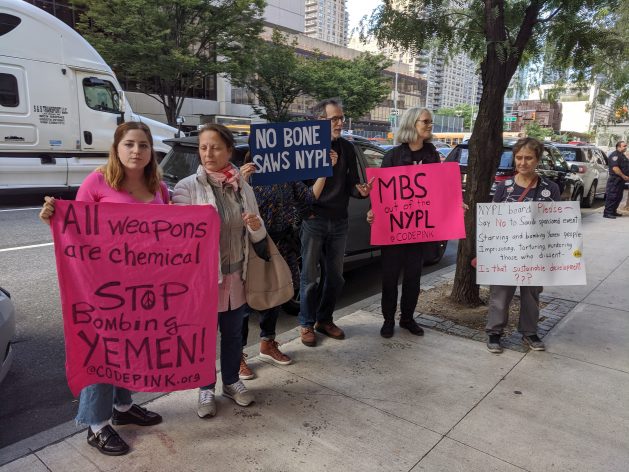

Protestors rallied outside a library building in Manhattan on Wednesday, carrying placards about Saudi Arabia’s war in Yemen and referencing the “bone saw” that was reportedly used to dismember Jamal Khashoggi, a prominent critic of Saudi prince Mohammad bin Salman. Credit: James Reinl/IPS
– A New York library appeared to bow to pressure this week when it canceled an event that was being co-hosted by Saudi Arabia’s crown prince Mohammad bin Salman, who is accused of a range of human rights abuses.
On Wednesday, the New York Public Library (NYPL) said it was scrapping the so-called Misk-OSGEY Youth Forum, a workshop on Sept. 23 that was being co-hosted by bin Salman’s Misk Foundation and U.N. youth envoy Jayathma Wickramanayake.
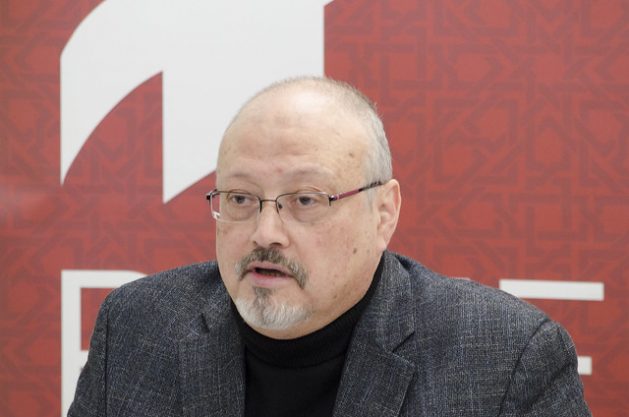
The event had been blasted by Human Rights Watch (HRW) and other campaign groups, who said it served to whitewash bin Salman’s reputation after the killing of Saudi journalist Jamal Khashoggi in October last year — reportedly on the crown prince’s orders.
Evan Chesler, chairman of the NYPL board, said that dropping the workshop was the “appropriate thing to do” after weeks of protests and an online petition that had garnered more than 7,000 signatures.
In a statement, the library said it had cancelled the “space rental” amid “concerns about possible disruption to library operations as well as the safety of our patrons” amid “public concern around the event and one of its sponsors”.
It remains unclear whether the Misk Foundation will seek an alternative venue for the workshop at short notice. A U.N. spokesman told IPS it was “up to Misk to provide information on whether the event will take place elsewhere or not”.
Saudi Arabia’s mission to the U.N. and the Misk Foundation declined to comment on the controversy.
Protestors rallied outside a library building in Manhattan on Wednesday, carrying placards about Saudi Arabia’s war in Yemen and referencing the “bone saw” that was reportedly used to dismember Khashoggi, a prominent critic of bin Salman.
“This week’s protests show that the public will not keep quiet while the leadership of the NYPL, a treasured repository of civilisation, hires our library out to the butcherer of Khashoggi,” Matthew Zadrozny, president of the Committee to Save the New York Public Library, told IPS.
“The NYPL leadership must explain to the public it serves who signed the deal with bin Salman’s foundation and why.”
Kenneth Roth, director of HRW, blasted the “repression-whitewashing event” on Twitter and asked U.N. secretary-general Antonio Guterres to scrap the partnership between his youth envoy, Wickramanayake, and the crown prince’s charity.
Now that the New York Public Library has withdrawn as a venue for the Saudi crown prince’s repression-whitewashing event https://t.co/JvGG6cyLd2 will UN chief @AntonioGuterres withdraw his youth envoy’s sponsorship before a replacement venue is found? https://t.co/ZA1Ctd8iIO
— Kenneth Roth (@KenRoth) 19 September 2019
Suzanne Nossel, CEO of rights group PEN America, said the library had made the “right choice”, addiing bin Salman’s government had “orchestrated the murder and dismemberment of journalist Jamal Khashoggi”.
“Hosting this event just days before the anniversary of Jamal’s killing would have been particularly appalling not just for his family, friends, and colleagues, but also for those currently being persecuted in the kingdom.”
Nossel also noted that the library “is the crown jewel of the literary community in New York” and it stands for “free exchange of ideas and free expression, qualities that the crown prince has repeatedly disdained in both words and actions”.
The NYPL event was set to see some 300 budding young entrepreneurs learn about green themes, corporate responsibility and other parts of the U.N.’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) agenda.
Khashoggi, a U.S.-based journalist who frequently criticised the Saudi government, was killed and dismembered on Oct. 2 last year after visiting the Saudi consulate in Istanbul, where he collecting documents for his wedding.
The CIA assessed that bin Salman had ordered Khashoggi’s killing. U.N. expert Agnes Callamard has described the death as a “premeditated execution,” and called for bin Salman and other high-ranking Saudis to be investigated.
Officials in Riyadh, who initially said Khashoggi had left the premises unharmed, now say the journalist was killed by a rogue hit squad that did not involve bin Salman. Activists have since pushed for accountability over the killing.