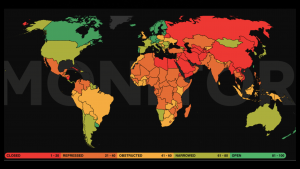

Several Southern African countries have or are in the process of enacting legislation that limits the civil society space, with implications for human rights. Credit: CIVICUS Monitor
By Busani Bafana
BULAWAYO, Jul 31 2023 (IPS)
Freedom of expression is under threat as governments in Southern Africa have enacted laws restricting civil society organizations, says global rights advocacy organisation, CIVICUS, warning that human rights violations are on the increase globally.
“The state of civil society is unfortunately not improving; civil restrictions continue across the world,” said David Kobe, the advocacy Lead at CIVICUS.
“More than 2 billion people live in countries that are rated as closed, which is the worst rating any country can have – this means that 28 percent of the world’s population are not able to speak out when there is corruption or human rights violations restrictions or cannot write articles as journalists without facing appraisals,” Kobe told IPS in an interview, noting that the organization’s human rights tool is indicating growing suppression of civil space across the world.
The CIVICUS Monitor, a tool accessing the state of civic space in more than 190 countries, provides evidence of restrictions on human rights by governments. The CIVICUS Monitor rates the state of civil space ‘open, ‘repressed’, and ‘closed’ according to each country.
Kobe notes that human rights violations are increasing globally with more restrictions on civil society in Australia, the United Kingdom and the United States. The picture is not different in the Southern Africa region where restrictions on civil space have been continuing, and these have included censorship, violent response to protests and restrictive laws as seen in Angola, Mozambique and Zimbabwe
Closing Civil Society Space
Zimbabwe remains on the CIVICUS Monitor Watchlist as attacks on civic space continue ahead of the scheduled 2023 national elections.
Last November, Zimbabwe approved the Criminal Law (Codification and Reform) Amendment Bill, 2022, known as the Patriotic Act. The law seeks to create the offence of “wilfully damaging the sovereignty and national interest of Zimbabwe” and will essentially criminalise the lobbying of foreign governments to extend or implement sanctions against Zimbabwe or its officials.
Furthermore, the Zimbabwe government gazetted the Private Voluntary Organisations Amendment Bill in November 2021, amending the Private Voluntary Organisations Act, which governs non-profit organizations. The main aim of the Bill is to comply with the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) recommendations to strengthen the country’s legal framework to combat money laundering, financing terrorism and proliferation.
Civil society organizations warn that the Bill could hinder their activities and financing with potential adverse impacts on economic development. Besides, NGOs argue that they are a low-risk sector with no precedence of financing terrorism and money laundering.
Musa Kika, Executive Director of Zimbabwe Human Rights NGO Forum, says the PVO will affect the operations of NGOs, including deterring donors from funding PVOs, fearing the money could end up under the grip of the government. Besides, the Bill has a provision giving the Minister of Justice unfettered powers to place under supervision or surveillance, using subjective discretion, those PVOs the Minister deems to be high risk.
“Continued hostility and harassment on the part of the government towards the work of CSOs in the country will thus only result in a hugely detrimental effect on their efforts in advancing the protection of and respect for the basic human rights and freedoms of ordinary Zimbabwean civilians as espoused under Zimbabwe’s Constitution,” Kika said. He noted that civil society organisations were operating in a tough environment in Zimbabwe where the government does not trust them, especially those working in the fields of governance and human rights.
“We have a government that does not want to account,” said Kika. “We have had many human rights activists who have been arrested on flimsy charges…Terrorism finance is being used as a cover, but the motive is to close the democratic space because the government and accountability in human rights and governance are sworn enemies.”
In Zimbabwe, NGOs have, in partnership with the government, supported development, providing a range of services in health, education, social protection, humanitarian assistance, environmental management, emergency response and democracy building. A research report commissioned by the Zimbabwe Human Rights NGO Forum in collaboration with the Southern Defenders and Accountability Lab has warned of huge job and financial losses if the Bill is passed into law.
United Nations experts have urged Zimbabwe’s President Emerson Mnangagwa to reject enacting a bill that would severely restrict civic space and the right to freedom of association in the country.
However, President Mnangagwa has defended the passage of the PVO Bill, vowing to speedily “sign it into law once it reaches my desk”. In a commentary in his weekly column published by the government-owned Sunday Mail, Mnangagwa said signing the bill into law will usher Zimbabwe into a “new era of genuine philanthropic and advocacy work, unsullied by ulterior political or financial motives.”
Mnangagwa said the law was meant to defend the country from foreign infiltration.
Engendering Patriotism but Endangering Democracy
Zimbabwe has also recently approved another repressive law known as the ‘Patriot Act’.
“The Patriotic Act is an extremely repressive and unconstitutional piece of legislation that has serious ramifications for citizens’ rights, particularly the rights of freedom of expression in the lead up to the elections,” human rights lawyer, Dough Coltart, tells IPS in an interview.
“There is a very real need to educate the citizens on what the ramifications of this Act are for people’s lives because the Act has far-reaching consequences for the entire country and will essentially stifle any public dialogue around the challenges we are facing as a country.”
“The Patriot law is a bad piece of legislation which is an affront to the practice of ethical journalism in Zimbabwe,” Njabulo Ncube, Coordinator of the Zimbabwe National Editors’ Forum (ZINEF), told IPS. “It stinks to the highest skies as it criminalizes the practice of good journalism. It is anti-media freedom and free expression…civil society organisations have also been caught in the mix; they cannot effectively make government account for its actions.”
Democracy Dimming
The situation in Zimbabwe is echoed in some countries across Southern Africa, where governments are cracking down on CSOs in the name of protecting national sovereignty and the threats of money laundering and terrorism financing.
In Angola, the country’s National Assembly, on May 25 2023, passed a draft NGO Statute, which CSOs have criticized for limiting freedom of association by giving the state excessive powers to interfere with civil society activities.
According to the Movimento de Defensores de Direitos Humanos de Angola (Movement of Human Rights Defenders of Angola, KUTAKESA), the government has targeted civil society with legislation that is meant for terrorists and money launderers, though it has never been proven in any court that a CSO has committed an act of terrorism in Angola.
On the contrary, the rationale of this legislation constitutes institutional terrorism, the target of which are CSOs, said Godinho Cristóvão, a jurist, human rights defender and executive director of KUTEKA in an interview with the CIVICUS Monitor.
“The Angolan authorities should have aligned themselves with the democratic rule of law and respected the work of CSOs and HRDs,” Cristóvão is quoted as saying.
“Instead, there has been an increase in threats, harassment and illegal arrests of human rights defenders who denounce or hold peaceful demonstrations against acts of bad governance and violations of citizens’ rights and freedoms. There have been clear setbacks with regard to the guarantee of fundamental rights and freedoms enshrined in the constitution, as well as the rights set out in the African Charter on Human and Peoples’ Rights and other human rights treaties Angola has ratified.”
In Mozambique, a new NGO on Anti-Money Laundering and Terrorist Financing Act, which overregulates CSOs, is seen as the death knell for the civic movement in the country. The Act was approved in October 2022 under the pretext of fighting terrorism. It has further curtailed freedoms of expression, information, press, assembly and public participation.
Paula Monjane, Executive Director of the Civil Society Learning and Capacity Building Centre (CESC), a Mozambican non-profit civil society organisation, said currently, the legislation was being proposed to silence dissenting voices and people fighting for better governance of public affairs and the protection of human rights in the country.
The draft Anti-Money Laundering and Terrorism Financing Act law establishes a legal regime for the creation, organisation and functioning of CSOs, and Monjane highlighted that it contains several norms that violate freedom of association despite this right being safeguarded by the constitution and international human rights treaties.
“It gives the government absolute and discretionary powers to ‘create’, control the functioning of, suspend and extinguish CSOs,” said Monjane, adding, “If the bill is approved, it will legitimise already existing practices restricting civic space, allowing the persecution of dissenting voices and organisations critical of the government, up to banning them from continuing to operate.”
Monjane said if the bill is passed into law CSOs in Mozambique will push for it to be declared unconstitutional and will ask the African Union, through the African Commission on Human and Peoples’ Rights, and the United Nations, through the Special Rapporteur on the rights to freedom of peaceful assembly and of association to urgently condemn it.
On actions to foster human rights and human rights defenders, Kobe said civil society organisations must be supported to hold governments accountable for upholding national and international human rights conventions that they have subscribed to.
The Universal Periodic Review, an assessment of the state of civic and human rights of a country over a four-year period, provides recommendations to governments enabling them to open civic space and remove restrictive laws.
“Governments need to implement the recommendations of the UPR and not treat them as a formality for them to be seen by the international community as respecting human rights when they are not,” said Kobe, adding that encouraging governments to implement the 2030 Agenda on Sustainable Development was also a way of getting them to see development alongside human rights.
IPS UN Bureau Report



















