Africa, Civil Society, Climate Change, Development & Aid, Energy, Environment, Featured, Food and Agriculture, Gender, Headlines, Sustainable Development Goals, TerraViva United Nations
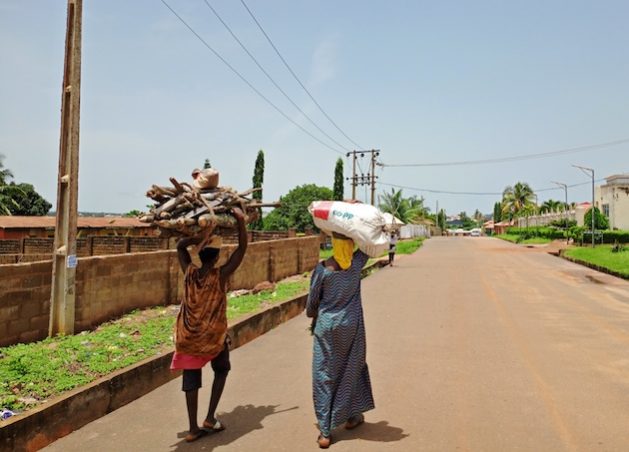

Nigerian women returning from the forest with firewood. Credit: Peace Oladipo/IPS
– One sunny mid-morning in Omu-Aran village, a community in Kwara State, North Central Nigeria, Iyabo Sunday sat beside a firewood stand observing her pot of beans with rice (a combination enjoyed by many in Nigeria).
The 52-year-old widow used her plastic dirt parker to fan the flames, occasionally blowing air through her mouth for speed and frantically shielding her face from the wisps of smoke that curled from the firewood.
After a hike in electricity tariffs, Sunday told IPS that she abandoned her electric-powered stove for cooking gas. But instability in the “economy has successfully caused me to move back to the firewood since my children and I must eat.”
Oyedele Christiana, a 41-year-old restaurateur who specializes in making fufu, a local delicacy made from cassava, expressed her wish to stop using firewood and charcoal but was constrained by finances. “The smoke enters my eyes and makes me cough a lot. I usually use firewood for my canteen business, while I use charcoal at home for household cooking.”
Like Iyabo, Christiana made use of cooking gas. The sporadic increase in the price of domestic gas has since pushed her to the traditional cooking method, with its attendant havoc on her eyes and lungs. “I am not as old as I look, but cooking has done this,” Oyedele sighed.
The price of cooking gas in Nigeria has soared wildly amid the country’s inflation woes. The removal of subsidy on petrol products, together with a depreciation of the naira, has resulted in a steep increase in the cost of food and transportation. This hike in the cost of living comes amid a minimum wage of N30,000 ($18), ranked among the lowest in the world, according to Picodi.
The price of 12.5 kg of cooking gas increased from N7,413. ($4) in 2022 to N16,875 ($10) in February 2024 across the country, a price just half the national minimum wage.
Implications on Women, Environment
Women living in grassroots communities who can no longer afford cooking gas have no choice but to bear the harsh method of cooking with firewood. Many, like Ajayi Omole, an octogenarian living in Akungba, a town in Ondo State, have made cooking with firewood a delight due to the lack of alternatives.
“We usually go into the forest, get the trees, sun dry (them), and prepare them for cooking.” However, she said, “I have a stove inside my room but I can’t use it because I don’t have enough to purchase kerosene.”
The nation’s alarming poverty circle, where Iyabo and Oyedele belong, speaks loudly about the reality of clean cooking. Statistics indicate that 63 percent of the entire population mostly relies on traditional method cooking, usually described as ‘dirty’.
The National Council on Climate Change (NCCC) has stated that, aside from the dangers of deforestation and climate destruction, the use of firewood and charcoal for cooking directly affects women’s health. This is in agreement with figures from the Federal Ministry of Environment about how more than 98,000 Nigerian women die annually from smoke inhaled while cooking with firewood.
Aisha Sulaiman, a renewable energy and green hydrogen technologist, said that rising prices of cooking gas have caused many to transition back to the use of firewood and charcoal, leading many women to multiple health issues. She emphasized that women suffer stronger health issues as secondhand smokers.
She said, “In an African setting, women belong to the kitchen; that’s how the narrative is, even if that is not supposed to be. In rural communities, the main source of energy in terms of cooking is the traditional method, which is unsustainable and harmful.
“The traditional methods of cooking involve charcoal and firewood. These are materials that lead to the release of greenhouse gases, particularly CO2, into our environment, and this in turn contributes to global warming, which brings about climate change.”
Speaking on women’s health, Sulaiman mentioned that respiratory diseases could stem from inhaling smoke from charcoal and firewood. “These methods are a source of air pollution, which can cause serious health issues. Overexposure to the smoke also leads to a disease called chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, which is very endemic to women,’’ she said. Sulaiman added that the Nigerian government should prioritize making clean energy accessible and cost-competitive to procure its acceptance by the people in low-income communities.
Ibrahim Muhammad, an energy consultant and team lead at Climate Alaramma Sustainable Development Initiative, a youth-led environmental organization in northern Nigeria, argued that the transition back to the traditional method of cooking would increase deforestation. He said the increase in LPG’s price is connected to the nation’s economic downturn.
In his words, “There is extensive research demonstrating the significant impact of traditional cooking methods on women and children. These methods contribute to deforestation and air pollution, particularly through the emission of smoke.”
Muhammad noted that women’s transition to traditional cooking was a setback in Nigeria’s transition plan to energy, especially in the area of clean cooking.
The Nigerian government and international development partners must find avenues for cleaning cooking infrastructure to be subsidized so that rural communities, mostly affected, can be able to afford it. According to him, “Considering the nature of some communities that are into agriculture, they are expected to be supported with infrastructure that can help them use this agricultural waste to cook. Additionally, the prices of these clean cooking stoves that are being developed are subsidized.”
Speaking further on alternatives, he added, “Briquettes, produced from agricultural waste, typically resemble charcoal and can perform all the functions of charcoal. They are energy-efficient and made from various agricultural waste materials, thus not promoting deforestation.”
Muhammad added that harmless solutions should be created to fit in Nigeria’s context; electric stoves may be considered impossible due to unstable electricity.
“Solar cookers are typically used when it is sunny, but many people hardly have lunch, they mostly focus on breakfast and dinner. Many women cook early in the morning or evening, so we need to tailor solutions to our specific circumstances,’’ he said.
IPS UN Bureau Report