Asia-Pacific, Civil Society, Climate Change, Climate Change Justice, Editors’ Choice, Environment, Featured, Food and Agriculture, Food Security and Nutrition, Headlines, Natural Resources, Sustainable Development Goals, TerraViva United Nations
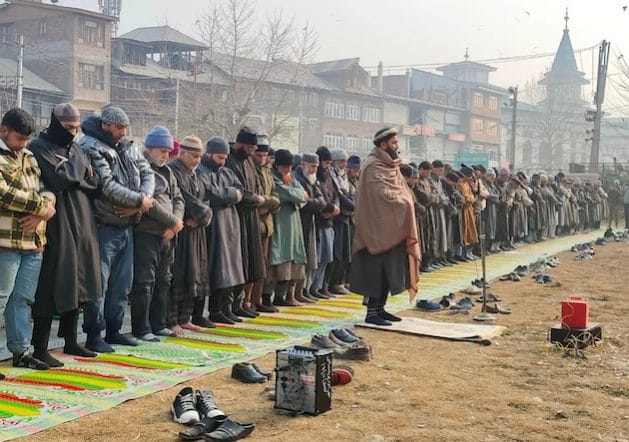

Local Muslims held special prayer ceremonies in January for snowfall. Credit: Umar Manzoor Shah/IPS
– Abdul Gani Malik, a 75-year-old goldsmith living in Kashmir’s capital, Srinagar, has witnessed eras of tranquility and turbulence in the Himalayan region. What he has not seen, however, is a snowless Kashmir during the winter.
Malik still works at his shop, located in one of the jam-packed markets of the old city area of Kashmir’s capital, intricately lacing colorful emeralds on dazzling gold necklaces. While conversing with IPS, he mentions that the winter in Kashmir has never been so terrible and terrifying as it has been this year.
He recalls how, during the 40-day harshest winter period from December 21 to January 30, snow would accumulate to about six or seven feet, freezing and making pathways treacherous even for city dwellers. In the mountainous region, according to Malik, the snow would last for several months, regulating temperatures during the summer and providing water and food.
“Now is a different tale. The mountains appear dry and dead. The rivers are carrying no water, and our woods are bereft of life. This is an absolute apocalypse,” Malik said.
The region of Kashmir is located in the north-western complex of the Himalayan ranges, with marked relief variation, snow-capped summits, antecedent drainage, complex geological structure, and rich temperate vegetation and fauna.
Kashmir’s winter is traditionally divided into three parts: Chilay Kalan (old man winter), Chilay Khuarud (young winter), and Chilay Bacha (kiddy winter). The coldest part, called Chilay Kalan, starts on December 21 and ends at the end of January. It is during this period that snowfall is expected.
“The temperatures during this period plummet to even minus 8 to 10 degrees Celsius, and when it snows, it accumulates in glaciers. The snowfall in the later period is of no use,” says Abdul Ghani Malik.
He was part of the congregational prayers held across Kashmir for snowfall. Local Muslims, who constitute more than 90 percent of the local population, decided in January to hold special prayers for snowfall in all major mosques. “We prayed, and we hope God listens to our plight.”
According to Abid Ali, a student of environmental sciences from Kashmir, Kashmir’s livelihood depends on snowfall, and if it doesn’t snow, things are going to take a terrible shape.
“The region’s electricity system, agriculture, and tourism are all dependent on snowfall. The dry winter will prove catastrophic for the local populace,” Abid said.
Kashmir, as per estimates, reported a 79 percent precipitation deficit through December of last year. Indian meteorologists claim that unusual weather is linked to global warming and El Niño, the sporadic climate phenomenon that can create warm, dry conditions in the Indian subcontinent and other parts of Asia.
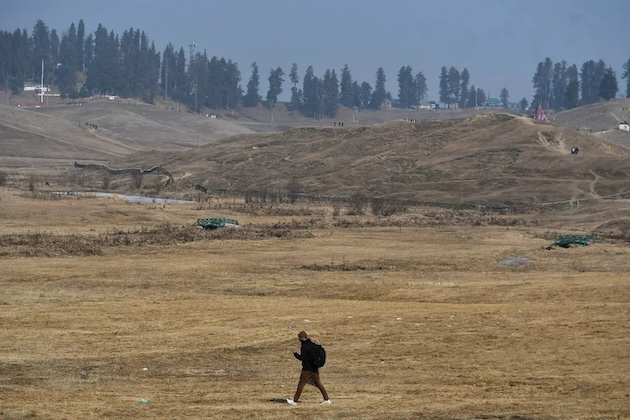

A man walks through an area in Kashmir where low snowfall is causing concern as the region’s economy is highly dependent on it. Credit: Umar Manzoor Shah/IPS
Threat to Agriculture
In Kashmir, 60 percent of the state’s revenue comes from agriculture and horticulture, and about 80 percent of the population lives in rural areas.
However, over the years, the valley has experienced irregular patterns of precipitation. In the first five months of 2022, Kashmir saw a 38 percent rain shortage, according to data provided by the Meteorological Department (MeT) in Srinagar.
The data reveals that the Kashmir Valley has experienced a significant lack of pre-monsoon precipitation over the years. From March 1 to May 31, 2022, the region got 99.5 mm of rain, 70 percent lower than average.
Comparatively, between March and May of each of the following years—2017, 2018, 2019, 2020, and 2021—there was a deficit of 16, 28, 35, and 26 percent, respectively. The dry winter this year is already throwing life out of gear for the farmers.
Abdul Karim Ganaie, a farmer hailing from south Kashmir’s Pulwama, says the threats are menacingly looming large, and people cannot do anything other than watch helplessly as the crisis unfolds.
When IPS contacted Choudhary Mohammad Iqbal, the director of agriculture in Kashmir, he stated that the department was closely monitoring the situation and would be issuing a warning to the farmers in the coming months.
“We accept that the situation is going to prove worrisome for Kashmir’s farming community, but we have to adopt a strategy to ensure minimal losses. We are working on that front,” Choudhary said.
Tourism under Cloud
The famous tourist destinations in Kashmir are also witnessing a dip in tourist arrivals, putting the people associated with this business in dire straits. In January, the famous tourist resorts recorded the lowest arrival of foreign and domestic tourists, with only 30 percent occupancy in hotels.
It snows at last but too little, too late!
Finally, in the first week of February, when the harshest 40-day-long spell was already over, it snowed in most of the areas of Kashmir. However, according to experts, the snow would yield the fewest results as it is not possible to accumulate for an extended period.
What is important, says Mehraj Ahmad, a research scholar working on climate change in Kashmir, is that the snow must accumulate in the higher reaches for as long as possible until the arrival of summers.
“The snowfall of February or March carries the least significance when compared with the snowfall of January. Therefore, we really are keeping our fingers crossed and praying for the safeguard of our lives against the dark, dreadful effects of climate change,” Ahmad said.
IPS UN Bureau Report
IPS UN Bureau, IPS UN Bureau Report, India, Kashmir